
China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine ›› 2026, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 837-850.doi: 10.16431/j.cnki.1671-7236.2026.02.029
• Genetics and Breeding • Previous Articles Next Articles
SONG Xingchao( ), MENG Jinzhu, ZHAO Yuanyuan, WU Zhenyang, AN Qingming(
), MENG Jinzhu, ZHAO Yuanyuan, WU Zhenyang, AN Qingming( )
)
Received:2025-08-13
Online:2026-02-20
Published:2026-01-27
Contact:
AN Qingming
E-mail:songxingchao_888@126.com;anqingming2009@163.com
CLC Number:
SONG Xingchao, MENG Jinzhu, ZHAO Yuanyuan, WU Zhenyang, AN Qingming. Analysis of Codon Usage Bias Patterns and Evolution of TYR Gene in Wumeng Black-bone Chickens[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2026, 53(2): 837-850.
Table 1
CDS information of TYR gene in different species"
序号 No. | 物种 Species | 科 Family | 属 Genus | 登录号 Accession No. | 序列长度 Sequence length/bp | 终止密码子 Stop codon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 乌蒙乌骨鸡 Wumeng Black-bone chickens | 雉科 Phasianidae | 原鸡属 Gallus | ON49713458 | 1 590 | TAA |
| 2 | 原鸡 Gallus gallus | 雉科 Phasianidae | 原鸡属 Gallus | NM_204160 | 1 590 | TAA |
| 3 | 日本鹌鹑 Coturnix japonica | 雉科 Phasianidae | 鹌鹑属 Coturnix | AB024278 | 1 590 | TAA |
| 4 | 水貂 Neovison vison | 鼬科 Mustelidae | 鼬属 Mustela | KJ716783 | 1 596 | TGA |
| 5 | 雪貂 Mustela putorius furo | 鼬科 Mustelidae | 貂属 Martes | XM_004796032 | 1 596 | TGA |
| 6 | 海豹 Leptonychotes weddellii | 海豹科 Phocidae | 海豹属 Leptonychotes | XM_006727372 | 1 596 | TAA |
| 7 | 猫 Felis catus | 猫科 Felidae | 猫属 Felis | XM_003992642 | 1 593 | TAA |
| 8 | 犬 Canis lupus familiaris | 犬科 Canidae | 犬属 Canis | NM_001002941 | 1 593 | TAA |
| 9 | 猪 Sus scrofa | 猪科 Suidae | 猪属 Sus | NM_001025212 | 1 596 | TAA |
| 10 | 羊驼 Vicugna pacos | 骆驼科 Camelidae | 小羊驼属 Vicugna | XM_006218369 | 1 593 | TAG |
| 11 | 山羊 Capra hircus | 牛科 Bovidae | 山羊属 Capra | NM_001287562 | 1 593 | TGA |
| 12 | 绵羊 Ovis aries | 牛科 Bovidae | 绵羊属 Ovis | NM_001130027 | 1 593 | TGA |
| 13 | 藏羚 Pantholops hodgsonii | 牛科 Bovidae | 藏羚属 Pantholops | XM_005970079 | 1 593 | TGA |
| 14 | 牛 Bos taurus | 牛科 Bovidae | 牛属 Bos | NM_181001 | 1 593 | TGA |
| 15 | 水牛 Bubalus bubalis | 牛科 Bovidae | 水牛属 Bubalus | JN887462 | 1 593 | TGA |
| 16 | 家马 Equus caballus | 马科 Equidae | 马属 Equus | XM_001492560 | 1 593 | TAA |
| 17 | 人 Homo sapiens | 人科 Hominidae | 人属 Homo | M27160 | 1 590 | TAA |
| 18 | 猕猴 Macaca mulatta | 猴科 Cercopithecidae | 猕猴属 Macaca | XM_001105033 | 1 593 | TAA |
| 19 | 小鼠 Mus musculus | 鼠科 Muridae | 鼠属 Mus | NM_011661 | 1 602 | TGA |
| 20 | 褐家鼠 Rattus norvegicus | 鼠科 Muridae | 家鼠属 Rattus | NM_001107535 | 1 593 | TGA |
| 21 | 斑马鱼 Danio rerio | 鲤科 Cyprinidae | 鲐属 Danio | NM_131013 | 1 608 | TGA |
| 22 | 鲤 Cyprinus carpio | 鲤科 Cyprinidae | 鲤属 Cyprinus | JQ670941 | 1 608 | TGA |
| 23 | 鲫 Carassius auratus | 鲤科 Cyprinidae | 鲫属 Carassius | DQ870906 | 1 608 | TGA |
Table 2
RSCU value of TYR gene in Wumeng Black-bone chickens"
氨基酸 Amino acids | 密码子 Codons | 数量 Number/个 | RSCU | 氨基酸 Amino acids | 密码子 Codons | 数量 Number /个 | RSCU | 氨基酸 Amino acids | 密码子 Codons | 数量 Number /个 | RSCU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ala(A) | 8 | Lys(K) | AAA | 4 | 0.62 | Arg(R) | 6 | ||||
| 11 | 9 | CGG | 2 | 0.36 | |||||||
| 10 | Leu(L) | TTA | 7 | 0.89 | Ser(S) | AGT | 4 | 0.59 | |||
| GCG | 1 | 0.13 | TTG | 4 | 0.51 | AGC | 6 | 0.88 | |||
| Cys(C) | TGT | 6 | 0.75 | 9 | TCT | 12 | 1.76 | ||||
| 10 | 11 | 8 | |||||||||
| Asp(D) | 13 | CTA | 3 | 0.38 | TCA | 11 | 1.61 | ||||
| GAC | 11 | 0.92 | CTG | 13 | 1.66 | TCG | 0 | 0 | |||
| Glu(E) | 17 | Met(M) | ATG | 13 | 1.00 | Thr(T) | ACT | 11 | 1.76 | ||
| GAG | 12 | 0.83 | Asn(N) | AAT | 16 | 0.91 | ACC | 6 | 0.96 | ||
| Phe(F) | TTT | 16 | 1.00 | 19 | ACA | 6 | 0.96 | ||||
| TTC | 16 | 1.00 | Pro(P) | 11 | ACG | 2 | 0.32 | ||||
| Gly(G) | GGT | 6 | 0.65 | 12 | Val(V) | GTT | 4 | 0.84 | |||
| 12 | CCA | 8 | 0.97 | 5 | |||||||
| 10 | CCG | 2 | 0.24 | GTA | 4 | 0.84 | |||||
| GGG | 9 | 0.97 | Gln(Q) | CAA | 11 | 0.88 | 6 | ||||
| His(H) | 7 | 14 | Trp(W) | TGG | 12 | 1.00 | |||||
| CAC | 6 | 0.92 | Arg(R) | AGA | 17 | 3.09 | Tyr(Y) | TAT | 9 | 0.82 | |
| Ile(I) | ATT | 5 | 0.50 | AGG | 4 | 0.73 | 13 | ||||
| ATC | 17 | 1.70 | CGT | 3 | 0.55 | * | TAA | 1 | 3.00 | ||
| ATA | 8 | 0.80 | CGC | 1 | 0.18 | * | TAG | 0 | 0 | ||
| * | TGA | 0 | 0 |
Table 3
Nucleotide composition of TYR gene codon in different species"
| 物种 | 核苷酸含量 Nucleotide contents | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | T3s | C3s | A3s | G3s | GC1s | GC2s | GC3s | GC12 | GC |
乌蒙乌骨鸡 Wumeng Black-bone chickens | 32.04 | 37.53 | 33.70 | 23.49 | 48.68 | 42.83 | 50.38 | 45.76 | 47.30 |
| 原鸡 Gallus gallus | 31.81 | 37.76 | 33.70 | 23.49 | 48.87 | 42.83 | 50.57 | 45.85 | 47.42 |
| 日本鹌鹑 Coturnix japonica | 30.43 | 38.44 | 33.97 | 23.58 | 47.67 | 43.40 | 51.32 | 45.54 | 47.67 |
| 水貂 Neovison vison | 34.40 | 37.59 | 26.61 | 27.46 | 50.56 | 43.42 | 53.57 | 46.99 | 49.19 |
| 雪貂 Mustela putorius furo | 33.11 | 38.81 | 27.02 | 27.68 | 51.13 | 42.86 | 54.32 | 47.00 | 49.44 |
| 海豹 Leptonychotes weddellii | 32.88 | 37.90 | 25.98 | 30.36 | 51.69 | 42.11 | 55.26 | 46.90 | 49.69 |
| 猫 Felis catus | 33.64 | 36.61 | 28.77 | 27.54 | 50.66 | 43.13 | 52.73 | 46.90 | 48.84 |
| 犬 Canis lupus familiaris | 34.93 | 35.16 | 30.53 | 26.05 | 50.85 | 43.13 | 50.47 | 46.99 | 48.15 |
| 猪 Sus scrofa | 31.89 | 37.81 | 29.83 | 26.84 | 50.75 | 43.61 | 53.20 | 47.18 | 49.19 |
| 羊驼 Vicugna pacos | 28.86 | 40.23 | 24.72 | 33.33 | 52.73 | 43.50 | 59.51 | 48.12 | 51.91 |
| 山羊 Capra hircus | 30.47 | 39.28 | 24.86 | 30.90 | 52.17 | 44.26 | 57.44 | 48.22 | 51.29 |
| 绵羊 Ovis aries | 31.15 | 38.37 | 25.69 | 30.32 | 51.98 | 44.26 | 56.31 | 48.12 | 50.85 |
| 藏羚 Pantholops hodgsonii | 31.15 | 39.05 | 25.83 | 29.24 | 51.98 | 43.69 | 56.31 | 47.84 | 50.66 |
| 牛 Bos taurus | 30.02 | 39.73 | 26.94 | 29.03 | 51.98 | 44.07 | 56.50 | 48.03 | 50.85 |
| 水牛 Bubalus bubalis | 31.07 | 39.00 | 27.58 | 28.24 | 52.17 | 43.50 | 55.37 | 47.84 | 50.35 |
| 家马 Equus caballus | 32.36 | 36.18 | 30.42 | 27.93 | 50.85 | 42.56 | 52.35 | 46.71 | 48.59 |
| 人 Homo sapiens | 34.41 | 34.41 | 30.99 | 27.63 | 49.43 | 42.45 | 50.94 | 45.94 | 47.61 |
| 猕猴 Macaca mulatta | 33.18 | 35.93 | 31.74 | 26.36 | 49.91 | 42.75 | 51.22 | 46.33 | 47.96 |
| 小鼠 Mus musculus | 35.75 | 33.26 | 33.33 | 24.70 | 48.31 | 42.70 | 47.75 | 45.51 | 46.25 |
| 褐家鼠 Rattus norvegicus | 36.53 | 32.42 | 35.03 | 23.19 | 48.78 | 42.75 | 46.33 | 45.77 | 45.95 |
| 斑马鱼 Danio rerio | 20.44 | 42.00 | 19.47 | 44.48 | 55.22 | 44.78 | 69.03 | 50.00 | 56.34 |
| 鲤 Cyprinus carpio | 20.84 | 43.24 | 17.82 | 43.38 | 55.22 | 45.52 | 69.78 | 50.37 | 56.84 |
| 鲫 Carassius auratus | 21.21 | 43.30 | 17.43 | 43.79 | 55.22 | 44.78 | 69.96 | 50.00 | 56.65 |
Table 4
Parameters of codon usage bias of TYR gene in in different species"
物种 Species | 密码子适 应指数 CAI | 密码子 偏爱指数 CBI | 最优密码子 使用频率 FOP | 有效密 码子数 ENC | 同义密码子数L_sym | 氨基 酸数 L_aa | 蛋白质 疏水性 GRAVY | 芳香族氨基酸频率 Aromo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乌蒙乌骨鸡 Wumeng Black-bone chickens | 0.204 | 0.025 | 0.437 | 54.57 | 504 | 529 | ―0.362760 | 0.124764 |
| 原鸡 Gallus gallus | 0.206 | 0.031 | 0.440 | 54.23 | 504 | 529 | ―0.362760 | 0.124764 |
| 日本鹌鹑 Coturnix japonica | 0.206 | 0.043 | 0.446 | 53.41 | 504 | 529 | ―0.364461 | 0.122873 |
| 水貂 Neovison vison | 0.210 | 0.022 | 0.433 | 57.15 | 503 | 531 | ―0.388889 | 0.126177 |
| 雪貂 Mustela putorius furo | 0.211 | 0.029 | 0.438 | 56.10 | 505 | 531 | ―0.374953 | 0.126177 |
| 海豹 Leptonychotes weddellii | 0.210 | 0.017 | 0.430 | 57.02 | 505 | 531 | ―0.361582 | 0.126177 |
| 猫 Felis catus | 0.201 | ―0.014 | 0.412 | 58.17 | 502 | 530 | ―0.329811 | 0.124528 |
| 犬 Canis lupus familiaris | 0.203 | ―0.016 | 0.412 | 56.04 | 503 | 530 | ―0.334906 | 0.124528 |
| 猪 Sus scrofa | 0.203 | 0.007 | 0.424 | 55.63 | 505 | 531 | ―0.344256 | 0.128060 |
| 羊驼 Vicugna pacos | 0.216 | 0.039 | 0.442 | 57.26 | 504 | 530 | ―0.399811 | 0.126415 |
| 山羊 Capra hircus | 0.224 | 0.081 | 0.465 | 57.27 | 505 | 530 | ―0.340566 | 0.128302 |
| 绵羊 Ovis aries | 0.220 | 0.057 | 0.451 | 57.46 | 505 | 530 | ―0.340566 | 0.128302 |
| 藏羚 Pantholops hodgsonii | 0.215 | 0.045 | 0.444 | 57.51 | 504 | 530 | ―0.324151 | 0.128302 |
| 牛 Bos taurus | 0.216 | 0.049 | 0.448 | 55.99 | 505 | 530 | ―0.348302 | 0.128302 |
| 水牛 Bubalus bubalis | 0.215 | 0.035 | 0.438 | 56.00 | 504 | 530 | ―0.343396 | 0.128302 |
| 家马 Equus caballus | 0.200 | ―0.006 | 0.415 | 58.68 | 506 | 530 | ―0.338868 | 0.133962 |
| 人 Homo sapiens | 0.200 | ―0.042 | 0.398 | 56.20 | 500 | 529 | ―0.356333 | 0.128544 |
| 猕猴 Macaca mulatta | 0.206 | ―0.024 | 0.410 | 55.74 | 502 | 530 | ―0.309623 | 0.128302 |
| 小鼠 Mus musculus | 0.199 | ―0.047 | 0.394 | 54.17 | 508 | 533 | ―0.347842 | 0.129456 |
| 褐家鼠 Rattus norvegicus | 0.197 | ―0.034 | 0.404 | 54.95 | 503 | 530 | ―0.381321 | 0.132075 |
| 斑马鱼 Danio rerio | 0.236 | 0.132 | 0.495 | 49.64 | 511 | 535 | ―0.259065 | 0.127103 |
| 鲤 Cyprinus carpio | 0.260 | 0.181 | 0.522 | 50.05 | 510 | 535 | ―0.280000 | 0.125234 |
| 鲫 Carassius auratus | 0.281 | 0.213 | 0.540 | 50.32 | 509 | 535 | ―0.326542 | 0.125234 |
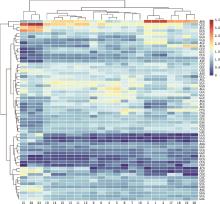
Fig.3
Clustering analysis of codon RSCU values of TYR gene in different species①1,Wumeng Black-bone chickens;2,Gallus gallus;3,Coturnix japonica;4,Neovison vison;5,Mustela putorius furo;6,Leptonychotes weddellii;7,Felis catus;8,Canis lupus familiaris;9,Sus scrofa;10,Vicugna pacos;11,Capra hircus;12,Ovis aries;13,Pantholops hodgsonii;14,Bos taurus;15,Bubalus bubalis;16,Equus caballus;17,Homo sapiens;18,Macaca mulatta;19,Mus musculus;20,Rattus norvegicus;21,Danio rerio;22,Cyprinus carpio;23,Carassius auratus. ②Each rectangular box represents RSCU value of a codon; The intensity of the color coding indicates different RSCU values"
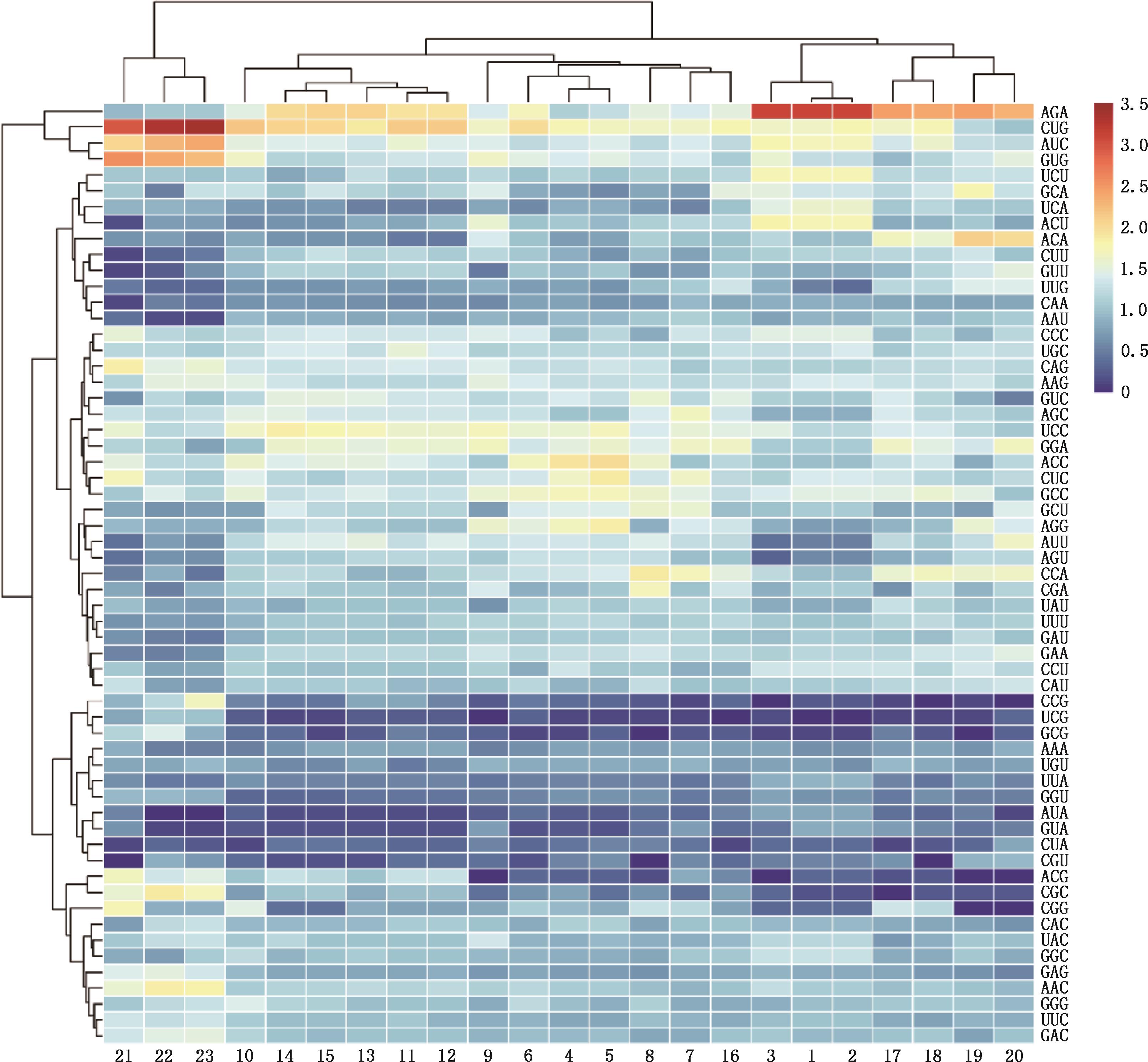
Table 5
Comparison of TYR gene codon usage bias between Wumeng Black-bone chickens and other model organisms"
密码子 Codons | 氨基酸 Amino acids | 乌蒙乌骨鸡 Wumeng Black-bone chickens (TYR) | 小鼠 Mus musculus (Mm) | 斑马鱼 Danio rerio (Dr) | 大肠杆菌 Escherichia coli (Ec) | F值 F-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TYR/Mm | TYR/Dr | TYR/Ec | ||||||
| TTT | Phe(F) | 30.19 | 17.20 | 18.20 | 22.10 | 1.76 | 1.66 | 1.37 |
| TTC | Phe(F) | 30.19 | 21.80 | 20.80 | 15.80 | 1.38 | 1.45 | 1.91 |
| TTA | Leu(L) | 13.21 | 6.70 | 7.00 | 13.80 | 1.97 | 1.89 | 0.96 |
| TTG | Leu(L) | 7.55 | 13.40 | 12.30 | 12.90 | 0.56 | 0.61 | 0.59 |
| CTT | Leu(L) | 16.98 | 13.40 | 12.70 | 11.40 | 1.27 | 1.34 | 1.49 |
| CTC | Leu(L) | 20.75 | 20.20 | 17.00 | 10.50 | 1.03 | 1.22 | 1.98 |
| CTA | Leu(L) | 5.66 | 8.10 | 6.20 | 3.90 | 0.70 | 0.91 | 1.45 |
| CTG | Leu(L) | 24.53 | 39.50 | 37.60 | 50.90 | 0.62 | 0.65 | 0.48 |
| ATT | Ile(I) | 9.43 | 15.40 | 16.50 | 29.40 | 0.61 | 0.57 | 0.32 |
| ATC | Ile(I) | 32.08 | 22.50 | 23.70 | 23.80 | 1.43 | 1.35 | 1.35 |
| ATA | Ile(I) | 15.09 | 7.40 | 7.70 | 5.60 | 2.04 | 1.96 | 2.69 |
| ATG | Met(M) | 24.53 | 22.80 | 25.50 | 27.10 | 1.08 | 0.96 | 0.91 |
| GTT | Val(V) | 7.55 | 10.70 | 14.10 | 18.00 | 0.71 | 0.54 | 0.42 |
| GTC | Val(V) | 9.43 | 15.40 | 14.80 | 14.70 | 0.61 | 0.64 | 0.64 |
| GTA | Val(V) | 7.55 | 7.40 | 6.70 | 10.90 | 1.02 | 1.13 | 0.69 |
| GTG | Val(V) | 11.32 | 28.40 | 28.30 | 26.10 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.43 |
| TCT | Ser(S) | 22.64 | 16.20 | 16.90 | 8.70 | 1.40 | 1.34 | 2.60 |
| TCC | Ser(S) | 15.09 | 18.10 | 15.20 | 9.00 | 0.83 | 0.99 | 1.68 |
| TCA | Ser(S) | 20.75 | 11.80 | 13.20 | 8.20 | 1.76 | 1.57 | 2.53 |
| TCG | Ser(S) | 0 | 4.20 | 5.60 | 8.80 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| CCT | Pro(P) | 20.75 | 18.40 | 16.60 | 7.30 | 1.13 | 1.25 | 2.84 |
| CCC | Pro(P) | 22.64 | 18.20 | 12.70 | 5.60 | 1.24 | 1.78 | 4.04 |
| CCA | Pro(P) | 15.09 | 17.30 | 15.70 | 8.40 | 0.87 | 0.96 | 1.80 |
| CCG | Pro(P) | 3.77 | 6.20 | 8.20 | 22.50 | 0.61 | 0.46 | 0.17 |
| ACT | Thr(T) | 20.75 | 13.70 | 14.50 | 9.10 | 1.51 | 1.43 | 2.28 |
| ACC | Thr(T) | 11.32 | 19.00 | 16.20 | 22.70 | 0.60 | 0.70 | 0.50 |
| ACA | Thr(T) | 11.32 | 16.00 | 17.00 | 8.20 | 0.71 | 0.67 | 1.38 |
| ACG | Thr(T) | 3.77 | 5.60 | 7.40 | 15.10 | 0.67 | 0.51 | 0.25 |
| GCT | Ala(A) | 15.09 | 20.00 | 20.90 | 15.40 | 0.75 | 0.72 | 0.98 |
| GCC | Ala(A) | 20.75 | 26.00 | 19.50 | 25.20 | 0.80 | 1.06 | 0.82 |
| GCA | Ala(A) | 18.87 | 15.80 | 16.60 | 20.70 | 1.19 | 1.14 | 0.91 |
| GCG | Ala(A) | 1.89 | 6.40 | 8.60 | 32.20 | 0.30 | 0.22 | 0.06 |
| TAT | Tyr(Y) | 16.98 | 12.20 | 12.60 | 16.50 | 1.39 | 1.35 | 1.03 |
| TAC | Tyr(Y) | 24.53 | 16.10 | 17.00 | 12.30 | 1.52 | 1.44 | 1.99 |
| CAT | His(H) | 13.21 | 10.60 | 10.90 | 12.80 | 1.25 | 1.21 | 1.03 |
| CAC | His(H) | 11.32 | 15.30 | 14.80 | 9.30 | 0.74 | 0.76 | 1.22 |
| CAA | Gln(Q) | 20.75 | 12.00 | 11.80 | 14.60 | 1.73 | 1.76 | 1.42 |
| CAG | Gln(Q) | 26.42 | 34.10 | 33.50 | 29.50 | 0.77 | 0.79 | 0.90 |
| AAT | Asn(N) | 30.19 | 15.60 | 16.30 | 19.10 | 1.94 | 1.85 | 1.58 |
| AAC | Asn(N) | 35.85 | 20.30 | 24.10 | 21.60 | 1.77 | 1.49 | 1.66 |
| AAA | Lys(K) | 7.55 | 21.90 | 29.30 | 34.00 | 0.34 | 0.26 | 0.22 |
| AAG | Lys(K) | 16.98 | 33.60 | 30.70 | 11.10 | 0.51 | 0.55 | 1.53 |
| GAT | Asp(D) | 24.53 | 21.00 | 24.80 | 32.80 | 1.17 | 0.99 | 0.75 |
| GAC | Asp(D) | 20.75 | 26.00 | 27.80 | 19.20 | 0.80 | 0.75 | 1.08 |
| GAA | Glu(E) | 32.08 | 27.00 | 24.40 | 39.20 | 1.19 | 1.31 | 0.82 |
| GAG | Glu(E) | 22.64 | 39.40 | 42.80 | 18.90 | 0.57 | 0.53 | 1.20 |
| TGT | Cys(C) | 11.32 | 11.40 | 11.30 | 5.30 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 2.14 |
| TGC | Cys(C) | 18.87 | 12.30 | 11.20 | 6.40 | 1.53 | 1.68 | 2.95 |
| TGG | Trp(W) | 22.64 | 12.50 | 11.60 | 15.30 | 1.81 | 1.95 | 1.48 |
| CGT | Arg(R) | 5.66 | 4.70 | 6.90 | 20.30 | 1.20 | 0.82 | 0.28 |
| CGC | Arg(R) | 1.89 | 9.40 | 9.60 | 20.90 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.09 |
| CGA | Arg(R) | 11.32 | 6.60 | 6.70 | 3.90 | 1.72 | 1.69 | 2.90 |
| CGG | Arg(R) | 3.77 | 10.20 | 6.60 | 6.40 | 0.37 | 0.57 | 0.59 |
| AGA | Arg(R) | 7.55 | 12.70 | 13.20 | 9.40 | 0.59 | 0.57 | 0.80 |
| AGG | Arg(R) | 11.32 | 19.70 | 18.40 | 16.00 | 0.57 | 0.62 | 0.71 |
| AGT | Ser(S) | 32.08 | 12.10 | 14.30 | 3.00 | 2.65 | 2.24 | 10.69 |
| AGC | Ser(S) | 7.55 | 12.20 | 10.20 | 1.90 | 0.62 | 0.74 | 3.97 |
| GGT | Gly(G) | 11.32 | 11.40 | 13.70 | 24.10 | 0.99 | 0.83 | 0.47 |
| GGC | Gly(G) | 22.64 | 21.20 | 17.20 | 27.90 | 1.07 | 1.32 | 0.81 |
| GGA | Gly(G) | 18.87 | 16.80 | 21.50 | 9.00 | 1.12 | 0.88 | 2.10 |
| GGG | Gly(G) | 16.98 | 15.20 | 10.00 | 11.90 | 1.12 | 1.70 | 1.43 |
| TAA | 1.89 | 1.00 | 1.10 | 1.90 | 1.89 | 1.72 | 0.99 | |
| TAG | 0 | 0.80 | 0.60 | 0.30 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| TGA | 0 | 1.60 | 1.40 | 1.10 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| [1] | SATO S, OTAKE T, SUZUKI C, et al. Mapping of the recessive white locus and analysis of the tyrosinase gene in chickens[J]. Poultry Science, 2007, 86(10): 2126-2133. |
| [2] | ANCANS J, TOBIN D J, HOOGDUIJN M J, et al. Melanosomal pH controls rate of melanogenesis, eumelanin/phaeomelanin ratio and melanosome maturation in melanocytes and melanoma cells[J]. Experimental Cell Research, 2001, 268(1): 26-35. |
| [3] | PANZELLA L, EBATO A, NAPOLITANO A, et al. The late stages of melanogenesis: Exploring the chemical facets and the application opportunities[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2018, 19(6): 1753. |
| [4] | NAM I S, OH M G, NAM M S, et al. Specific mutations in the genes of MC1R and TYR have an important influence on the determination of pheomelanin pigmentation in Korean native chickens[J]. Journal of Advanced Veterinary and Animal Research, 2021, 8(2): 266-273. |
| [5] | WANG Y, LI S M, HUANG J, et al. Mutations of TYR and MITF genes are associated with plumage colour phenotypes in geese[J]. Asian-Australasian Journal of Animal Sciences, 2014, 27(6): 778-783. |
| [6] | GUIMARÃES-MOREIRA M, MARQUES C I, AFONSO S, et al. A missense mutation in the tyrosinase gene explains acromelanism in domesticated canaries[J]. Animal Genetics, 2024, 55(6): 838-842. |
| [7] | CHO E, KIM M, MANJULA P, et al. A retroviral insertion in the tyrosinase (TYR) gene is associated with the recessive white plumage color in the Yeonsan Ogye chicken[J]. Journal of Animal Science and Technology, 2021, 63(4): 751-758. |
| [8] | YU S, WANG G, LIAO J, et al. Five alternative splicing variants of the TYR gene and their different roles in melanogenesis in the Muchuan Black-boned chicken[J]. British Poultry Science, 2019, 60(1): 8-14. |
| [9] | YANG J, LIU X, ZHANG J, et al. Molecular cloning and biochemical analysis of tyrosinase from the crested ibis in China[J]. Biochemical Genetics, 2012, 50(11-12): 936-945. |
| [10] | 徐志强,李丰耘,赵净颖,等. 武定乌骨鸡TYR基因多态性与黑色素沉积的关联研究[J]. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学),2021,36(4):608-615. |
| XU Z Q, LI F Y, ZHAO J Y, et al. The association between TYR gene polymorphism and melanin deposition in Wuding Black-boned chicken[J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University (Natural Science), 2021, 36(4): 608-615. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 祖盘玉,李 维,林家栋,等. 赤水乌骨鸡TYR基因多态性及生物信息学分析[J]. 南方农业学报,2019,50(12):2806-2811. |
| ZU P Y, LI W, LIN J D, et al. Polymorphism and bioinformatics analysis of TYR gene in Chishui Black-bone chicken[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2019, 50(12): 2806-2811. (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 陆晓屏, 滕召纯, 李庆华, 等.他留乌骨鸡TYR基因多态性与色素性状相关性分析[J]. 中国家禽, 2015, 37(17):17-22. |
| LU X P, TENE Z C, LI Q H, et al. Associations of TYR gene polymorphisms with pigment traits in Taliu Black-bone chicken[J]. China Poultry, 2015, 37(17): 17-22. (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | YU S, WANG G, LIAO J, et al. Identification of key microRNAs affecting melanogenesis of breast muscle in Muchuan Black-boned chickens by RNA sequencing[J]. British Poultry Science, 2020, 61(3): 1466-1799. |
| [14] | 郑嫩珠,李 丽,辛清武,等. 酪氨酸酶(TYR)、小眼畸形相关转录因子(MITF)和刺鼠信号蛋白(ASIP)基因对白绒乌骨鸡黑色素沉积的遗传效应[J]. 农业生物技术学报,2015,23(8):1076-1083. |
| ZHENG N Z, LI L, XIN Q W, et al. Genetic effect of tyrosinase(TYR), microphthalmia-associated transcription factor(MITF)and agouti signaling protein(ASIP) genes on melanin deposition of White Sillky fowl (Gallus gallus domesticus brisson)[J]. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2015,23(8):1076-1083. (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | PARVATHY S T, UDAYASURIYAN V, BHADANA V. Codon usage bias[J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 2022, 49(1): 539-565. |
| [16] | LYU X L, YANG Q, ZHAO F Z, et al. Codon usage and protein length-dependent feedback from translation elongation regulates translation initiation and elongation speed[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2021, 49(16): 9404-9423. |
| [17] | XIE Q, CHEN X, MA H, et al. Improved gene therapy for spinal muscular atrophy in mice using codon-optimized hSMN1 transgene and hSMN1 gene-derived promotor[J]. EMBO Molecular Medicine, 2024, 16(4): 945-965. |
| [18] | 孙 鹏,朱爱臣,梁 天,等. 鸡IL-17基因的克隆、序列分析及密码子优化提高表达水平[J]. 农业生物技术学报, 2023, 31(7): 1464-1476. |
| SUN P, ZHU A C, LIANG T, et al. Cloning, sequence analysis and codon optimization of chicken (Gallus gallus) IL-17 gene to improve the expression level[J]. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2023, 31(7): 1464-1476. (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | 宋兴超,王云艳,孟金柱,等. 乌蒙乌骨鸡TYR基因启动子区克隆及分子结构特征分析[J]. 中国畜牧杂志,2024,60(12):215-223. |
| SONG X C, WANG Y Y, MENG J Z, et al. Cloning and analysis of molecular structure characteristics of promoter region sequence of TYR gene in Wumeng Black-bone chicken[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2024, 60(12): 215-223. (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | BÉNITIÈRE F, LEFÉBURE T, DURET L. Variation in the fitness impact of translationally optimal codons among animals[J]. Genome Research, 2025, 35(3): 446-458. |
| [21] | 李 鑫,李 伟,刘 洁,等. 乌苏里貉MC3R基因密码子偏好性分析[J]. 中国畜牧兽医,2024,51(4):1349-1361. |
| LI X, LI W, LIU J, et al. Analysis of codon usage bias of MC3R gene in Nyctereutes procyonoides [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2024, 51(4): 1349-1361. (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | NICZYPORUK J S, KOZDRUN W, CZEKAJ H, et al. Characterisation of Adenovirus strains represented species B and E isolated from broiler chicken flocks in Eastern Poland[J]. Heliyon, 2021, 7(2): e06225. |
| [23] | XU Q, CAO J, RAI K R, et al. Codon usage bias of goose circovirus and its adaptation to host[J]. Poultry Science, 2024, 103(7): 103775. |
| [24] | RAHMAN S U, ABDULLAH M, KHAN A W, et al. A detailed comparative analysis of codon usage bias in Alongshan virus[J]. Virus Research, 2022, 308: 198646. |
| [25] | 张小丹,牛 熙,许 瑶,等. 猪蛋白质二硫化物异构酶A4基因克隆及密码子偏好性分析[J]. 中国畜牧兽医,2019,46(4):1074-1085. |
| ZHANG X D, NIU X, XU Y, et al. Cloning and codon-preference analysis of protein disulfide isomerase A4 gene in pig[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2019, 46(4): 1074-1085. (in Chinese) | |
| [26] | 吴宪明,吴松锋,任大明,等. 密码子偏性的分析方法及相关研究进展[J]. 遗传,2007,29(4):420-426. |
| WU X M, WU S F, REN D M, et al. The analysis method and progress in the study of codon bias[J]. Hereditas, 2007, 29(4): 420-426. (in Chinese) | |
| [27] | MAZUMDER T H, CHAKRABORTY S. Gaining insights into the codon usage patterns of TP53 gene across eight mammalian species[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(3): e0121709. |
| [28] | JIANG Y, DENG F, WANG H, et al. An extensive analysis on the global codon usage pattern of baculoviruses[J]. Archives of Virology, 2008, 153(12): 2273-2282. |
| [29] | 冯海悦,张 羽,吴正常,等. 13种哺乳动物MUC4基因密码子使用模式分析[J]. 农业生物技术学报,2018,26(9):1546-1556. |
| FENG H Y, ZHANG Y, WU Z C, et al. Analisis of codon usage patterns of MUC4 gene in 13 species of mammals[J]. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2018, 26(9): 1546-1556. (in Chinese) | |
| [30] | 何志敏,朱肖霞,余清婷,等. 鲤科鱼类SP1密码子的偏好性与进化[J]. 水产学报,2025,49(2):52-63. |
| HE Z M, ZHU X X, YU Q T, et al. Codon preference and evolutionary analysis of SP1 in Cyprinidae[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2025, 49(2): 52-63. (in Chinese) | |
| [31] | DILUCCA M, PAVLOPOULOU A, GEORGAKILAS A G, et al. Codon usage bias in radioresistant bacteria[J]. Gene, 2020, 742: 144554. |
| [32] | 张 涛,张跟喜,韩昆鹏,等. 京海黄鸡MyoG基因密码子特性分析[J]. 华北农学报,2014,29(4):71-79. |
| ZHANG T, ZHANG G X, HAN K P, et al. Characterization of codon usage of MyoG gene in Jinghai Yellow chicken[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-sinica, 2014, 29(4): 71-79. (in Chinese) | |
| [33] | SHEN Y Y, LIANG L, SUN Y B, et al. A mitogenomic perspective on the ancient, rapid radiation in the Galliformes with an emphasis on the Phasianidae[J]. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 2010, 132(10):1-10. |
| [34] | HUNT R C, SIMHADRI V L, IANDOLI M, et al. Exposing synonymous mutations[J]. Trends in Genetics, 2014, 30(7): 308-321. |
| [35] | RAO Y, WU G, WANG Z, et al. Mutation bias is the driving force of codon usage in the Gallus gallus genome[J]. DNA Research, 2011, 18(6): 499-512. |
| [36] | HE Z, DING S, GUO J, et al. Synonymous codon usage analysis of three Narcissus potyviruses[J]. Viruses, 2022, 14(5): 846. |
| [37] | SUEOKA N. Translation-coupled violation of parity rule 2 in human genes is not the cause of heterogeneity of the DNA G+C content of third codon position[J]. Gene, 1999, 238(1): 53-58. |
| [38] | TAYLOR T L, DIMITROV K M, AFONSO C L. Genome-wide analysis reveals class and gene specific codon usage adaptation in Avian paramyxoviruses 1[J]. Infection Genetics and Evolution, 2017, 50: 28-37. |
| [39] | LI H, ZHANG P, LI D,et al. The expression patterns of exogenous plant miRNAs in chickens[J]. Genes(Basel),2023, 14(3):760. |
| [40] | UDDIN A, CHOUDHURY M N, CHAKRABORTY S. Codon usage bias and phylogenetic analysis of mitochondrial ND1 gene in pisces, aves, and mammals[J]. Mitochondrial DNA Part A, 2018, 29(1): 36-48. |
| [41] | FAGES-LARTAUD M, HUNDVIN K, HOHMANN-MARRIOTT M F. Mechanisms governing codon usage bias and the implications for protein expression in the chloroplast of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii [J]. Plant Journal, 2022, 112(4): 919-945. |
| [42] | RANI S, MAMATHASHREE M N, BHARTHI I U, et al. Comprehensive examination on codon usage bias pattern of the Bovine ephemeral fever virus[J]. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 2024, 42(20): 10593-10603. |
| [1] | ZHANG Mengping, LIN Mingxin, WU Zhongliang, LUO Jingfei, CHEN Shanduier, WU Qiong. Analysis of mtDNA Codon Usage Bias in Shitan Chickens and Native Chicken Breeds of China [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2025, 52(12): 5772-5784. |
| [2] | LI Xin, LI Wei, LIU Jie, CHENG Jingran, LIU Jinjun, WANG Pengran, HAN Xueliang, REN Erjun, DENG Lufang, ZONG Wenli. Analysis of Codon Usage Bias of MC3R Gene in Nyctereutes procyonoides [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2024, 51(4): 1349-1361. |
| [3] | DAI Kaiyu, YANG Zhifeng, GUO Yexing. Analysis of Codon Usage Bias of Toll-like Receptor 5 Gene in 15 Species [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2024, 51(1): 11-22. |
| [4] | SUN Shouhu, CHEN Zhifei, GUO Zhixuan, YU Ting, WANG Xiuwu, LI Songbei, WEI Wenkang, HE Dongsheng. Study on Codon Usage Bias of N gene of Three Porcine Coronaviruses and Their Host Adaptive Mechanism [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2023, 50(6): 2403-2413. |
| [5] | SUN Yingxia, ZHANG Tieying, AN Jing, ZHENG Mengli. The Recombinant Expression of Laccase from Ganoderma lucidum in Aspergillus niger and the Key Factors Affecting Enzyme Production by Fermentation [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2022, 49(11): 4218-4227. |
| [6] | WANG Xiaolan, WU Shenji, HUANG Jinqiang, LI Yongjuan, PAN Yucai, ZHANG Qian. Bioinformatics and Expression Analysis of Tyrosinase Gene at the Different Stages and Tissues of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2021, 48(5): 1516-1524. |
| [7] | DAI Kaiyu, HUANG Yanjie, WU Lisi, BAO Wenbin, WU Shenglong. Analysis and Optimization of Codon Usage Bias of Porcine FUT2 Gene [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2018, 45(7): 1863-1872. |
| [8] | FAN Xin-yang, OUYANG Yi-na, WANG Peng-wu, ZHANG Yong-yun, TENG Xiao-hong, MIAO Yong-wang. Analysis of Codon Usage Bias of Leptin Receptor Gene in Buffalo [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2017, 44(4): 1069-1078. |
| [9] | LIU Zhong-na, ZHONG Jin-cheng, CHAI Zhi-xin, MA Zhi-jie, ZENG Xian-bin, SONG Qiao-qiao. Cloning and Sequence Analysis of SRY Gene in Maiwa Yak [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2013, 40(12): 5-11. |
| [10] | ZHANG Chun-xiang;JIANG Yu-suo. Research Advances on Molecular Evolution and Signal Transduction of Odorant Receptor of Insects [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2011, 38(5): 66-69. |
| [11] | YU Zhan- qiao; YANG Fang; ZHANG Ri- jun. Advances on Heterologous Expression of Bacteriocins [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2010, 37(2): 51-54. |
| [12] | YANG Fang;YU Zhan-qiao;ZHANG Ri-jun. Heterologly Expression of Plantaricin GenesPlnE and PlnF in E.coli [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2010, 37(12): 55-59. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||