
China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine ›› 2026, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 973-983.doi: 10.16431/j.cnki.1671-7236.2026.02.041
• Preventive Veterinary Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Mengdi1( ), ZHANG Miaoxiang1, ZENG Yubing1, LIANG Yanjiao1, HUANG Teng1, HUANG Jianni1,2,3(
), ZHANG Miaoxiang1, ZENG Yubing1, LIANG Yanjiao1, HUANG Teng1, HUANG Jianni1,2,3( )
)
Received:2025-05-07
Online:2026-02-20
Published:2026-01-27
Contact:
HUANG Jianni
E-mail:mengdi42370@163.com;jiannihuang@gxu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
WANG Mengdi, ZHANG Miaoxiang, ZENG Yubing, LIANG Yanjiao, HUANG Teng, HUANG Jianni. Expression of Chicken DDX21 Protein and Preparation and Application of Its Polyclonal Antibody[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2026, 53(2): 973-983.
Table 1
Amino acid sequence similarity analysis of the DEXDc,HELICc and GUCT domains of DDX21 protein in chicken and other species"
物种 Species | DEXDc结构域 DEXDc domain | HELICc结构域 HELICc domain | GUCT结构域 GUCT domain |
|---|---|---|---|
| 人 Homo sapiens | 82.7 | 88.0 | 58.3 |
| 猕猴Macaca mulatta | 82.2 | 88.0 | 58.3 |
| 野猪Sus scrofa | 83.6 | 85.5 | 60.4 |
| 水牛Bos tauus | 81.7 | 86.7 | 53.1 |
| 绵羊Ovis aries | 81.7 | 88.0 | 58.3 |
| 北极狐Vulpes lagopus | 86.6 | 88.0 | 60.4 |
| 大鼠Rattus norvegicus | 85.1 | 89.2 | 56.2 |
| 小鼠Mus musculus | 85.1 | 89.2 | 56.2 |
| 绿头鸭Anas platyrhynchos | 95.7 | 100 | 89.6 |
| 卡氏夜鹰Antrostomus carolinensis | 94.2 | 97.6 | 82.3 |
| 斑鸠Nothoprocta perdicaria | 94.3 | 91.6 | 62.5 |
| 鳜鱼Siniperca chuatsix | 78.4 | 88.0 | 60.4 |
| 斑马鱼Danio rerio | 80.0 | 86.7 | 53.1 |
| 泰国斗鱼Betta splendens | 76.0 | 86.7 | 47.9 |
| 非洲爪蟾Xenopus tropicalis | 65.9 | 69.9 | 47.9 |
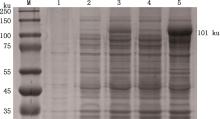
Fig.11
SDS-PAGE analysis of induced expression of chicken DDX21 recombinant proteinM, NcmColor Prestained Protein Marker (14-250 ku); 1, Bacterial culture of empty vector; 2, Bacterial culture of recombinant protein without induction; 3, Bacterial culture of recombinant protein after induction; 4, Supernatant of sonicated bacterial culture after induction; 5, Pellet of sonicated bacterial culture after induction"
Fig.12
Western blotting analysis of induced expression of chicken DDX21 recombinant proteinM, Broad Range Rainbow Molecular Weight Marker (10-130 ku); 1, Bacterial culture of empty vector; 2, Bacterial culture of recombinant protein without induction; 3, Bacterial culture of recombinant protein after induction; 4, Supernatant of sonicated bacterial culture after induction; 5, Pellet of sonicated bacterial culture after induction"
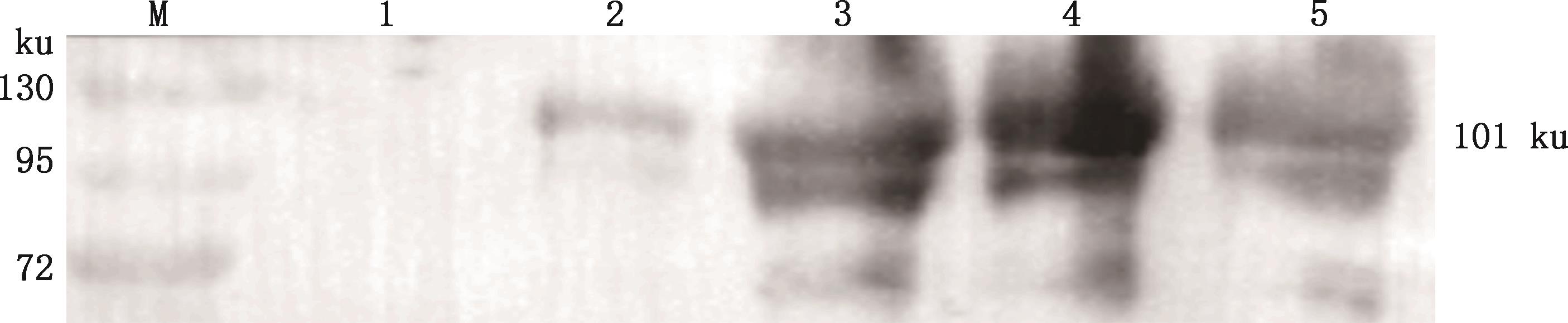
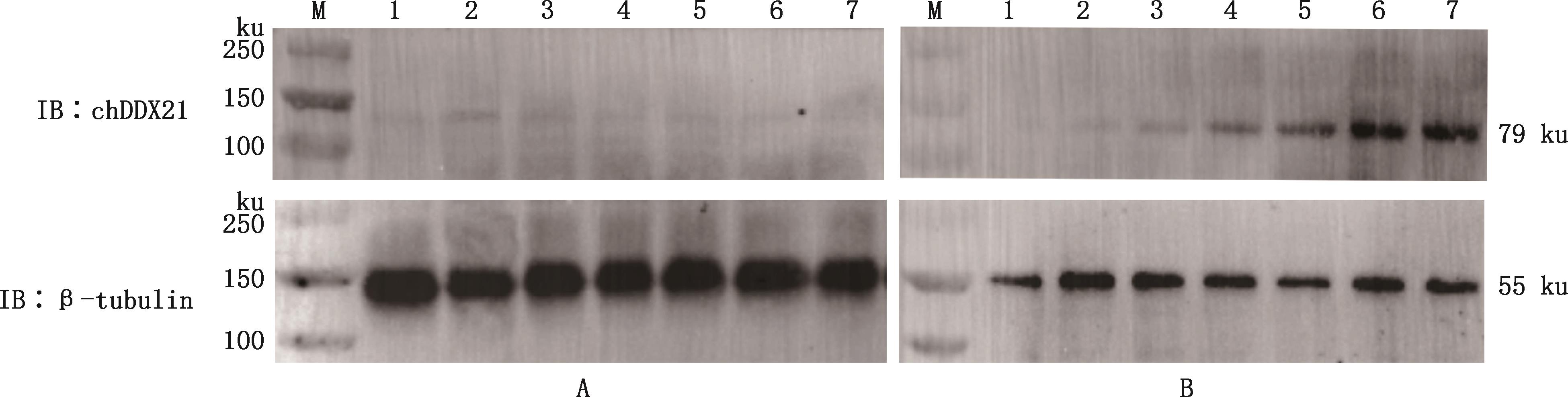
Fig.15
Western blotting analysis of expression of DDX21 protein in tissues of healthy and infected chickens①A, The expression of DDX21 protein in tissues of healthy chickens; B, The expression of DDX21 protein in tissues of chickens infected with H9N2 subtype AIV. ②M, Broad Range Rainbow Molecular Weight Marker (10-130 ku); 1, Bursa of Fabricius; 2, Liver; 3, Lung; 4, Heart; 5, Thymus; 6, Brain; 7, Spleen"
| [1] | HONDELE M, SACHDEV R, HEINRICH S, et al. DEAD-box ATPases are global regulators of phase-separated organelles[J]. Nature, 2019, 573(7772): 144-148. |
| [2] | PARTHUN M, LONG M E, HEMANN E A. Established and emerging roles of DEAD/H-box helicases in regulating infection and immunity[J]. Immunological Reviews, 2025, 329(1): e13426. |
| [3] | HAO J D, LIU Q L, LIU M X, et al. DDX21 mediates co-transcriptional RNA m6A modification to promote transcription termination and genome stability[J]. Molecular Cell, 2024, 84(9): 1711-1726. |
| [4] | SINGLETON M R, DILLINGHAM M S, WIGLEY D B. Structure and mechanism of helicases and nucleic acid translocases[J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 2007, 76: 23-50. |
| [5] | JANKOWSKY E. RNA helicases at work: Binding and rearranging[J]. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 2011, 36(1): 19-29. |
| [6] | DE BORTOLI F, ESPINOSA S, ZHAO R. DEAH-Box RNA helicases in pre-mRNA splicing[J]. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 2021, 46(3): 225-238. |
| [7] | WU M, XU G, HAN C, et al. lncRNA SLERT controls phase separation of FC/DFCs to facilitate PolⅠtranscription[J]. Science, 2021, 373(6554): 547-555. |
| [8] | JI C, ZHONG Q, SU H, et al. DDX21 is a potential biomarker for predicting recurrence and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Analytical Cellular Pathology, 2025, 2025: 1018820. |
| [9] | LU P, YU Z, WANG K, et al. DDX21 interacts with WDR5 to promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation by activating CDK1 expression[J]. Journal of Cancer, 2022, 13(5): 1530-1539. |
| [10] | WU S, SUN X, HUA R, et al. DDX21 functions as a potential novel oncopromoter in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A comprehensive analysis of the DExD box family[J]. Discover Oncology, 2024, 15(1): 333. |
| [11] | XIAO Y, FAN J, LI Z, et al. DDX21 at the nexus of RNA metabolism, cancer oncogenesis, and host-virus crosstalk: Decoding its biomarker potential and therapeutic implications[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2024, 25(24): 13581. |
| [12] | ULLAH R, LI J, FANG P, et al. DEAD/H-box helicases: Anti-viral and pro-viral roles during infections[J]. Virus Research, 2022, 309: 198658. |
| [13] | LI J, FANG P, ZHOU Y, et al. DEAD-box RNA helicase 21 negatively regulates cytosolic RNA-mediated innate immune signaling[J]. Frontiers in Immunology, 2022, 13: 956794. |
| [14] | BONAVENTURE B, GOUJON C. DExH/D-box helicases at the frontline of intrinsic and innate immunity against viral infections[J]. Journal of General Virology, 2022, 103(8): doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001766. |
| [15] | WU W, QU Y, YU S, et al. Caspase-dependent cleavage of DDX21 suppresses host innate immunity[J]. mBio, 2021, 12(3): e0100521. |
| [16] | ZHANG Z, KIM T, BAO M, et al. DDX1, DDX21, and DHX36 helicases form a complex with the adaptor molecule TRIF to sense dsRNA in dendritic cells[J]. Immunity, 2011, 34(6): 866-878. |
| [17] | CHEN Z, LI Z, HU X, et al. Structural basis of human helicase DDX21 in RNA binding, unwinding, and antiviral signal activation[J]. Advanced Science, 2020, 7(14): 2000532. |
| [18] | DONG Y, YE W, YANG J, et al. DDX21 translocates from nucleus to cytoplasm and stimulates the innate immune response due to Dengue virus infection[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2016, 473(2): 648-653. |
| [19] | ZHAO K, GUO X R, LIU S F, et al. 2B and 3C proteins of Senecavirus A antagonize the antiviral activity of DDX21 via the caspase-dependent degradation of DDX21[J]. Frontiers in Immunology, 2022, 13: 951984. |
| [20] | LIANG Y. Pathogenicity and virulence of influenza[J]. Virulence, 2023, 14(1): 2223057. |
| [21] | 谢 艳, 张 倩, 刘娜女, 等. DDX21 RNA解旋酶不同结构域的功能特点解析[J]. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2019, 35(4): 446-456. |
| XIE Y, ZHANG Q, LIU N N, et al. Functional analysis of different domains of DDX21 RNA helicase[J]. Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2019, 35(4): 446-456. (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 谢立兰, 安 康, 陈 力, 等. 猪DDX21基因的克隆、序列分析及原核表达[J]. 华北农学报, 2017, 32(3): 42-47. |
| XIE L L, AN K, CHEN L, et al. Cloning, sequence analysis, and prokaryotic expression of the porcine DDX21 gene[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2017, 32(3): 42-47. (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | VALDEZ B C, WANG W. Mouse RNA helicase Ⅱ/Gu: cDNA and genomic sequences, chromosomal localization, and regulation of expression[J]. Genomics, 2000, 66(2): 184-194. |
| [24] | MARCAIDA M J, KAUZLARIC A, DUPERREX A, et al. The human RNA helicase DDX21 presents a dimerization interface necessary for helicase activity[J]. iScience, 2020, 23(12): 101811. |
| [25] | DAUBNER G M, CLÉRY A, ALLAIN F H. RRM-RNA recognition: NMR or crystallography and new findings[J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2013,23(1):100-108. |
| [26] | CHEN G, LIU C, ZHOU L, et al. Cellular DDX21 RNA helicase inhibits Influenza A virus replication but is counteracted by the viral NS1 protein[J]. Cell Host & Microbe, 2014,15(4):484-493. |
| [27] | LI C, LI M, HU M, et al. Engineering Escherichia coli for the efficient biosynthesis of 6'-sialyllactose[J]. Food Bioscience, 2023, 55: 103040. |
| [28] | CHEN Z, WANG Z, ZHAO X, et al. Pathogenicity of different H5N6 highly pathogenic Avian influenza virus strains and host immune responses in chickens[J]. Veterinary Microbiology, 2020, 246: 108745. |
| [29] | WU S, HUANG J, HUANG Q, et al. Host innate immune response of geese infected with clade 2.3.4.4 H5N6 highly pathogenic Avian influenza viruses[J]. Microorganisms, 2020, 8(2): 224. |
| [1] | ZHANG Zhiying, HU Xiaodi, PENG Su, ZHANG Xingyue, SHE Peining, HUANG Xiaojie, SHI Dayou. Effects of LPS on the Growth Performance, Serum Biochemistry and Intestinal Health of Mahuang Chickens [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2026, 53(2): 659-670. |
| [2] | TANG Li, ZHANG Min, LI Jun, LIU Jinni, DENG Kaiwei, LIANG Chengcheng, HE Shuhai, WU Haigang, CHEN Hui, LI Yifan, GONG Qimeng, WU Dongke. Effects of Green Tea Aqueous Extract on Slaughter Performance, Meat quality and Serum Biochemical Indices of Cyan-shank Partridge Chickens [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2026, 53(2): 798-809. |
| [3] | SONG Xingchao, MENG Jinzhu, ZHAO Yuanyuan, WU Zhenyang, AN Qingming. Analysis of Codon Usage Bias Patterns and Evolution of TYR Gene in Wumeng Black-bone Chickens [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2026, 53(2): 837-850. |
| [4] | Hailu FAN, Siyu HUANG, Xin HE, Hongliang ZHANG, Bo ZHANG, Peng SHANG, Hao ZHANG. Comparative Analysis of Egg Quality During Peak Laying Period in Different Local Chicken Breeds [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2026, 53(1): 201-211. |
| [5] | Bingkun LIANG, Zhen WANG, Ziyu LIU, Dawei YAN, Xinxing DONG, Jiawei ZHU. Sequence Characteristics and Tissue Expression of SCARB2 Gene in Lijiang Pigs [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2026, 53(1): 343-358. |
| [6] | Pingyuan YANG, Xiaoman OU, Zhengmiao OU, Fenfen CHEN. Effect of HMOX1 Gene Overexpression on the Proliferation of Primary Preadipocyte in Wuliangshan Black-boned Chicken [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2026, 53(1): 359-367. |
| [7] | Zhongqi ZHAO, Mengmeng ZOU, Yunjing ZHANG, Lixia HE, Songshan WU, Xinxin ZHANG, Guijun YANG, Guangxing LI. Preparation and Identification of Polyclonal Antibody for Goose Astrovirus ORF2 Protein [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2026, 53(1): 368-377. |
| [8] | Shaoshuai ZHANG, Haoliang CHAI, Hongzhi WU, Guanyu HOU, Minhong ZHANG. Heat Stress Impacts on Thermoregulation, Production Performance, and Organismal Health in Chickens: Research Advance [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2026, 53(1): 39-48. |
| [9] | YUE Yuan, MA Guangzhan, GUO Siyan, WANG Jianjun, HUANG Bingjian, LU Ya, LYU Zengpeng, ZHANG Bingkun. A Comparative Study on the Effects of Two Immune Stress Models on Growth Performance and Intestinal Immune Status of Broiler Chickens [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2025, 52(9): 4032-4042. |
| [10] | CHEN Wanhong, YANG Wenpeng, HUANG Shaohua, ZHU Peiji, JIA Daihan, ZHAO Minmeng, ZHANG Jun, LI Jun, GONG Daoqing. Effects of Different Energy and Protein Levels Diets on the Growth Performance of Offspring of Snowy Mountain Chicken Breeder Hens [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2025, 52(9): 4057-4068. |
| [11] | FAN Qiuli, GOU Zhongyong, WANG Yitong, CUI Yan, LUO Qili, YE Jinling, LIN Xiajing, WANG Yibing, JIANG Shouqun. Effects of Fermented Mixed Meal on Growth Performance,Plasma Biochemical Indices and Meat Quality of Medium-growing Yellow-feathered Chickens [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2025, 52(9): 4069-4081. |
| [12] | CUI Yan, JIANG Shouqun, FAN Qiuli, LIN Xiajing, DING Fayuan, GAO Kaiguo, GOU Zhongyong. Effects of Whole Wheat-based Diet on Growth Performance and Meat Quality of Yellow-feathered Chickens [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2025, 52(9): 4136-4145. |
| [13] | LI Huan, OU Jiancun, HUANG Jian, QI Qien, ZHU Cui, LONG Lina, FENG Xin, WANG Wenhe, HUANG Weilong, ZHANG Huihua. Study on the Metabolizable Energy and Crude Protein Requirements of Qingyuan Partridge Chickens from 1 to 30 Days [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2025, 52(8): 3595-3606. |
| [14] | ZHANG Shuohan, LIU Yifan, XIE Binghong, SHAN Yanju, TU Yunjie, GAN Dafeng, XUE Fuguang, PEI Guoliang, ZHAO Haojian, WU Hongxiang, SHU Jingting. Study on Egg Quality and Nutrient Components of Major Local Chicken Breeds in Southern China [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2025, 52(8): 3642-3650. |
| [15] | HE Qiang, JIANG Xiaoxiang, FANG Tingting, LI Li, ZHANG Shouquan, WEI Hengxi. Effect of Different Glycerol Removal Methods on Artificial Insemination of Cryopreserved Chicken Semen [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2025, 52(8): 3707-3714. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||