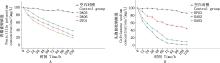
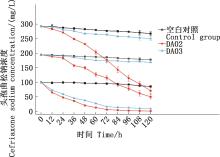
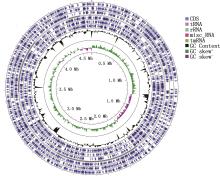
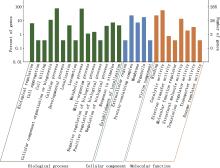
| [1] |
LI F, WANG C, ZHAO Z, et al. Pathway of typical β-lactam antibiotics degradation by black soldierfly and response characteristic of its intestinal microbes[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2025, 419: 132067.
|
| [2] |
CHEN S, WANG J, FENG H, et al. Quantitative study on the fate of antibiotic emissions in China[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2020, 42(10): 3471-3479.
|
| [3] |
KUMAR M, JAISWAL S, SODHI K K, et al. Antibiotics bioremediation: Perspectives on its ecotoxicity and resistance[J]. Environment International, 2019, 124: 448-461.
|
| [4] |
ZHAO Q, JIANG Z, LI T, et al. Current status and trends in antimicrobial use in food animals in China, 2018-2020[J]. One Health Advances, 2023, 1(1): 29.
|
| [5] |
STA ANA K M, MADRIAGA J, ESPINO M P, et al. β-lactam antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in Asian lakes and rivers: An overview of contamination, sources and detection methods[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 275: 116624.
|
| [6] |
LI S, SHI W Z, LI H M, et al. Antibiotics in water and sediments of rivers and coastal area of Zhuhai city, Pearl River estuary, South China[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 636: 1009-1019.
|
| [7] |
YANG J, ZHAO Z Q, WANG M, et al. Biodegradation of tylosin in swine wastewater by Providencia stuartii TYL-Y13: Performance, pathway, genetic background, and risk assessment[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 440: 129716.
|
| [8] |
ZHANG S, LIU Y, MOHISN A, et al. Biodegradation of penicillin G sodium by Sphingobacterium sp. SQW1: Performance, degradation mechanism, and key enzymes[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2024, 468: 133485.
|
| [9] |
YAN L, YAN N, GAO X Y, et al. Degradation of amoxicillin by newly isolated Bosea sp. Ads-6[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 828: 154411.
|
| [10] |
HOSSEINI H, AL-JABRI H M, MOHEIMANI N R, et al. Marine microbial bioprospecting: Exploitation of marine biodiversity towards biotechnological applications—A review[J]. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 2022, 62(9): 1030-1043.
|
| [11] |
ADENAYA A, BERGER M, BRINKHOFF T, et al. Usage of antibiotics in aquaculture and the impact on coastal waters[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2023, 188: 114645.
|
| [12] |
MURALIDHARAN M, GAYATHRI K V, KUMAR P S, et al. Mixed polyaromatic hydrocarbon degradation by halotolerant bacterial strains from marine environment and its metabolic pathway[J]. Environmental Research, 2022, 216(2): 114464.
|
| [13] |
吕银萍, 赵 玲, 靳永柯, 等. 海洋中氨氮降解菌的筛选鉴定及生长条件优化[J]. 环境保护科学, 2025, 51(4): 28-36.
|
|
LYU Y P, ZHAO L, JIN Y K, et al. Screening and identification of ammonia nitrogen-degrading bacteria from marine environment and optimization of their growth conditions[J]. Environmental Protection Science, 2025, 51(4): 28-36.(in Chinese)
|
| [14] |
李珍珍. 具有石油降解能力的海洋解磷菌的筛选及其特性研究[D]. 舟山:浙江海洋大学, 2024.
|
|
LI Z Z. Screening and characterization of marine phosphate-solubilizing bacteria with petroleum degradation ability[D]. Zhoushan: Zhejiang Ocean University,2024.(in Chinese)
|
| [15] |
FEIJOO P, MARÍN A, SAFONT E S, et al. Marine degradation of plastics in Western Mediterranean Sea: Comparison between biodegradable and conventional polymers[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2025, 234: 111222.
|
| [16] |
马浩天, 李 杨, 余梦博, 等. 海水中细菌的分离鉴定及其对动物源病原菌的抑菌活性研究[J]. 中兽医医药杂志, 2024, 43(1): 8-12.
|
|
MA H T, LI Y, YU M B, et al. Isolation and identification of bacteria in seawater and their antibacterial activity on animal pathogens[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Veterinary Medicine, 2024, 43(1): 8-12.(in Chinese)
|
| [17] |
马浩天, 李 杨, 余梦博, 等. 产细菌素贝莱斯芽孢杆菌CM7-4全基因组测序及抑菌活性研究[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2024, 51(12): 5117-5127.
|
|
MA H T, LI Y, YU M B, et al. Whole genome sequencing of bacteriocin-producing Bacillus velezensis CM7-4 and its bacteriostatic activity[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2024, 51(12): 5117-5127.(in Chinese)
|
| [18] |
GRANT J R, ENNS E, MARINIER E, et al. Proksee: In-depth characterization and visualization of bacterial genomes[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2023, 51(W1): W484-W492.
|
| [19] |
余梦博, 马浩天, 李 杨, 等. 1株贝莱斯芽孢杆菌G02全基因组测序分析[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2025, 52(5): 1977-1986.
|
|
YU M B, MA H T, LI Y, et al. Whole genome sequencing analysis of a strain of Bacillus velezensis G02[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2025, 52(5): 1977-1986.(in Chinese)
|
| [20] |
刘志旭, 韩文昌, 李彦芹, 等. 山东地区隐性乳房炎牛乳中β-内酰胺酶blaZ基因与微生物相关性研究[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2025, 52(5): 2318-2327.
|
|
LI Z X, HAN W C, LI Y Q, et al. Study on the correlation between β-lactase blaZ gene and microorganisms in milk of cows with latent mastitis in Shandong region[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2025, 52(5): 2318-2327.(in Chinese)
|
| [21] |
KAMALA K, SIVAPERUMAL P. Predominance of multi-drug resistant extended spectrum β lactamase producing bacteria from marine fishes[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2023, 323: 121314.
|
| [22] |
BROOKE J S. Advances in the microbiology of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia [J]. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 2021, 34(3): e0003019.
|
| [23] |
DELSHAD S T, SOLTANIAN S, SHARIFIYAZDI H, et al. Identification of N-acyl homoserine lactone-degrading bacteria isolated from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss)[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2018, 125(2): 356-369.
|
| [24] |
HINCHLIFFE P, CALVOPIÑA K, RABE P, et al. Interactions of hydrolyzed β-lactams with the L1 metallo-β-lactamase: Crystallography supports stereoselective binding of cephem/carbapenem products[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2023, 299(5): 104606.
|
| [25] |
LENG Y F, BAO J G, CHANG G F, et al. Biotransformation of tetracycline by a novel bacterial strain Stenotrophomonas maltophilia DT1[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 318: 125-133.
|
| [26] |
KAWAUCHI R, TADA T, SHERCHAN J B, et al. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia from Nepal producing two novel antibiotic inactivating enzymes, a Class A β-lactamase KBL-1 and an aminoglycoside 6'-N-acetyltransferase AAC(6')-Ⅰap[J]. Microbiology Spectrum, 2022, 10(4): e0114322.
|
| [27] |
PENG J, XIE X, FAN T, et al. Optimization of culture conditions for endophytic bacteria in mangrove plants and isolation and identification of bacteriocin[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2024, 15: 1429423.
|
| [28] |
LI H, WAN Q, ZHANG S D, et al. Housefly larvae (Musca domestica) significantly accelerates degradation of monensin by altering the structure and abundance of the associated bacterial community[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 170: 418-426.
|
| [29] |
WU X, ZHANG C, AN H, et al. Biological removal of deltamethrin in contaminated water, soils and vegetables by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia XQ08[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 279: 130622.
|
| [30] |
ZHANG X, HUANG Y, CHEN W J, et al. Environmental occurrence, toxicity concerns, and biodegradation of neonicotinoid insecticides[J]. Environmental Research, 2022, 218: 114953.
|
| [31] |
ALI S, HASSAN M, ESSAM T, et al. Biodegradation of aflatoxin by bacterial species isolated from poultry farms[J]. Toxicon, 2021, 195: 7-16.
|
| [32] |
QU F, CHEN Q, DING Y, et al. Isolation of a feather-degrading strain of bacterium from spider gut and the purification and identification of its three key enzymes[J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 2018, 45(6): 1681-1689.
|
| [33] |
SUBRAMANIAN K, BALARAMAN D, PANANGAL M, et al. Bioconversion of chitin waste through Stenotrophomonas maltophilia for production of chitin derivatives as a seabass enrichment diet[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12(1): 4792.
|
| [34] |
ALCAIDE M, STOGIOS P J, LAFRAYA Á, et al. Pressure adaptation is linked to thermal adaptation in salt-saturated marine habitats[J]. Environmental Microbiology,2015, 17(2): 332-345.
|
| [35] |
ABBOTT I J, SLAVIN M A, TURNIDGE J D, et al. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: Emerging disease patterns and challenges for treatment[J]. Expert Review of Anti-infective Therapy, 2011, 9(4): 471-488.
|
| [36] |
LOONEY W J, NARITA M, MÜHLEMANN K. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: An emerging opportunist human pathogen[J]. The Lancet Infectious Diseases, 2009, 9(5): 312-323.
|
| [37] |
KALIDASAN V, JOSEPH N, KUMAR S, et al. Iron and virulence in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: All we know so far[J]. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 2018, 8: 401.
|
| [38] |
OHNO T, HARADA S, SAITO H, et al. Molecular epidemiology and clinical features of Klebsiella variicola bloodstream infection compared with infection with other Klebsiella pneumoniae species complex strains[J]. Microbiology Spectrum, 2025, 13(6): e0301724.
|
| [39] |
YANG L, YANG K. Biological function of Klebsiella variicola and its effect on the rhizosphere soil of maize seedlings[J]. PeerJ, 2020, 8: e9894.
|
| [40] |
WANG D, SUN L, YIN Z, et al. Insights into genomic evolution and the potential genetic basis of Klebsiella variicola subsp. variicola ZH07 reveal its potential for plant growth promotion and autotoxin degradation[J]. Microbiology Spectrum, 2022, 10(6): e0084622.
|
| [41] |
DURAN-BEDOLLA J, GARZA-RAMOS U, RODRÍGUEZ-MEDINA N, et al. Exploring the environmental traits and applications of Klebsiella variicola [J]. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology, 2021, 52(4): 2233-2245.
|
| [42] |
USSO T A, MARR C M. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae [J]. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 2019, 32(3): e00001-19.
|
 ), 潘瑞雪, 龙赟而, 林倩倩, 伍诗韵, 彭金菊, 马驿(
), 潘瑞雪, 龙赟而, 林倩倩, 伍诗韵, 彭金菊, 马驿( )
)
 ), PAN Ruixue, LONG Yuner, LIN Qianqian, WU Shiyun, PENG Jinju, MA Yi(
), PAN Ruixue, LONG Yuner, LIN Qianqian, WU Shiyun, PENG Jinju, MA Yi( )
)