
China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine ›› 2026, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (1): 266-275.doi: 10.16431/j.cnki.1671-7236.2026.01.024
• Nutrition and Feed • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Furong1,2( ), FENG Xiaohui2, FENG Shengnan2, ZHANG Zhengjie2, WANG Yujiao2, MENG Qingshi2(
), FENG Xiaohui2, FENG Shengnan2, ZHANG Zhengjie2, WANG Yujiao2, MENG Qingshi2( ), ZHANG Chunxiang1(
), ZHANG Chunxiang1( )
)
Received:2025-04-02
Online:2026-01-05
Published:2025-12-26
Contact:
MENG Qingshi, ZHANG Chunxiang
E-mail:wangfurong0131@163.com;mengqingshi@caas.cn;chunxiangzhang@sxau.edu.cn
CLC Number:
WANG Furong, FENG Xiaohui, FENG Shengnan, ZHANG Zhengjie, WANG Yujiao, MENG Qingshi, ZHANG Chunxiang. Quantification of Sterculic Acid Based on Chemical Derivatization and Mass Spectrometry Technology[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2026, 53(1): 266-275.
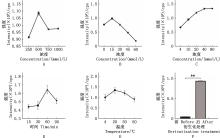
Fig.1
Comparison of the derivatization efficiency of sterculic acid under different reaction conditions①A, Optimization of EDC concentration; B, Optimization of HOAt concentration; C, Optimization of 2-pyridinecarbohydrazide concentration; D, Optimization of reaction time; E, Optimization of reaction temperature; F, Sensitivity evaluation before and after sterculic acid derivatization reaction. ②**, Extremely significant difference (P<0.05). The same as below"

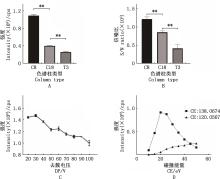
Fig.2
Optimization of chromatographic and mass spectrometric conditions for sterculic acidA, The influence of different chromatographic columns on the peak height of sterculic acid derivatives; B, The influence of different chromatographic columns on the signal-to-noise ratio of sterculic acid derivatives; C, The influence of different declustering potentials on the peak area of sterculic acid derivatives; D, The influence of different collision energies on the peak area of sterculic acid derivatives"
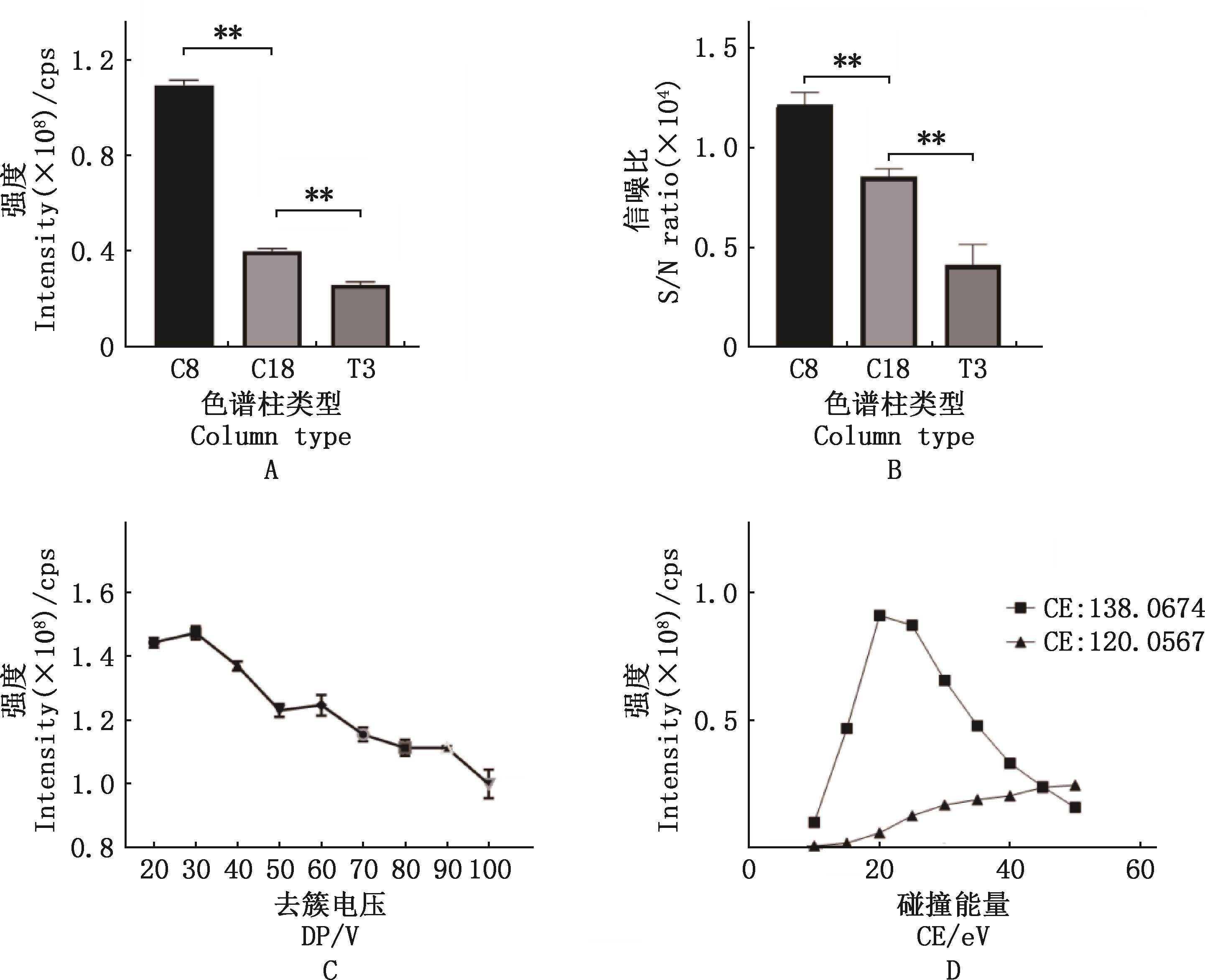
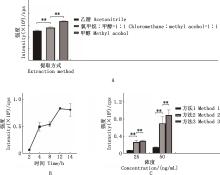
Fig.3
Optimization of sample pretreatment methodA, Effect of different methods on the peak area of free sterculic acid. B, The effect of different hydrolysis times on the peak area of esterified sterculic acid. C, Effect of different extraction methods on the peak area of esterified sterculic acid"
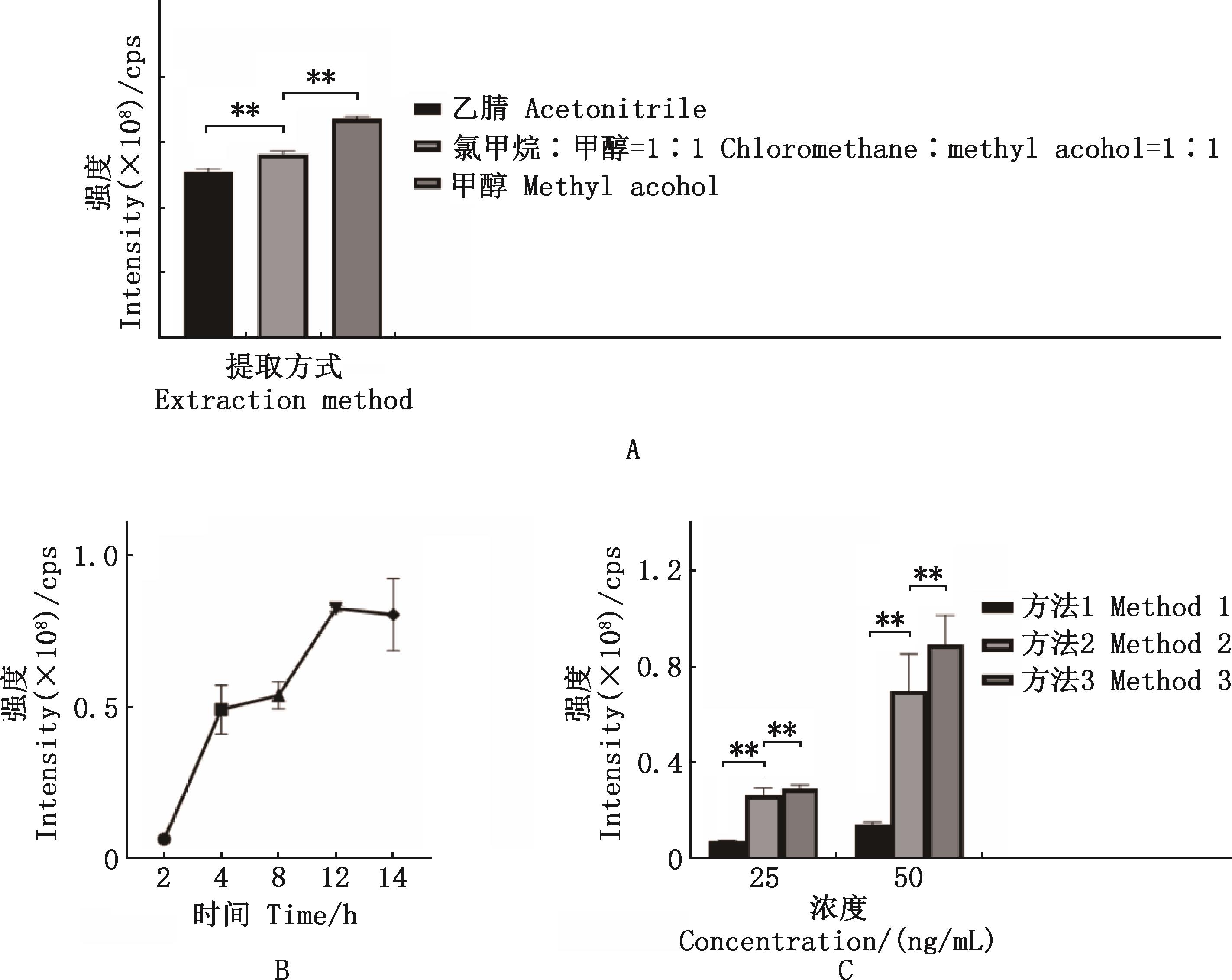
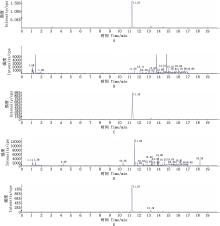
Fig.4
The chromatogram of sterculic acid and blank matrixA, Chromatogram of sterculic acid standard (250 ng/mL); B, Chromatogram of blank matrix for free sterculic acid; C, Chromatogram of blank matrix spiked with free sterculic acid (250 ng/mL); D, Chromatogram of blank matrix for esterified sterculic acid; E, Chromatogram of blank matrix spiked with esterified sterculic acid (250 ng/mL)"

Table 1
The precision of the method"
项目 Items | 苹婆酸浓度 Concentration of sterculic acid/(μg/kg) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12.5 | 25 | 50 | ||||
批内 Intra-assay | 批间 Inter-assay | 批内 Intra-assay | 批间 Inter-assay | 批内 Intra-assay | 批间 Inter-assay | |
游离态苹婆酸的RSD RSD of free sterculic acid | 1.57 | 2.38 | 1.01 | 1.94 | 2.21 | 1.61 |
结合态苹婆酸的RSD RSD of esterified sterculic acid | 1.77 | 4.28 | 0.79 | 6.22 | 2.01 | 3.40 |
Table 2
Quantification results of sterculic acid in feed samples"
样品 Sample | 游离态苹婆酸 Free sterculic acid | 结合态苹婆酸 Esterified sterculic acid |
|---|---|---|
| 棉油 Cottonseed oil | 29.72±2.48 | 1 812.76±475.47 |
| 棉粕 Cure cottonseed meal | 0.46±0.01 | 25.96±2.39 |
| 脱酚棉粕 Degossypoled cottonseed meal | 0.60±0.05 | 24.13±5.21 |
| 棉籽蛋白 Cottonseed protein | 0.09±0.02 | 12.14±1.75 |
| [1] | ZINN R A, MONTAÑO M, ALVAREZ E, et al. Feeding value of cottonseed meal for feedlot cattle[J]. Journal of Animal Science, 1997, 75(9): 2317-2322. |
| [2] | LIU X, ZOU D, WANG Y, et al. Replacement of fish meal with cottonseed protein concentrate in Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis): Nutrient digestibility, growth performance, free amino acid profile, and expression of genes related to nutrient metabolism[J]. Animal Nutrition, 2024, 12: 447-462. |
| [3] | PELÁEZ R, PARIENTE A, PÉREZ-SALA Á, et al. Sterculic acid: The mechanisms of action beyond stearoyl-CoA desaturase inhibition and therapeutic opportunities in human diseases[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(1): 140-159. |
| [4] | AO Y, CONG Z, BEIYU Z, et al. Effects of dietary cottonseed oil and cottonseed meal supplementation on liver lipid content, fatty acid profile and hepatic function in laying hens[J]. Animals, 2021, 11(1): 78-90. |
| [5] | YANG M, LUOYI Z, AO Y, et al. The effects of dietary cottonseed meal and oil supplementation on laying performance and egg quality of laying hens[J]. Food Science & Nutrition, 2019, 7(7): 2436-2447. |
| [6] | 穆杨. 棉籽油和棉籽粕在鸡“橡皮蛋”形成中的作用及机制研究[D].武汉: 华中农业大学, 2019. |
| MU Y. Study on the effect and mechanism of cottonseed oil and cottonseed meal on the formation of “rubber eggs”[D].Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2019.(in Chinese) | |
| [7] | TAO A, WANG J, LUO B, et al. Research progress on cottonseed meal as a protein source in pig nutrition: An updated review[J]. Animal Nutrition, 2024, 25: 220-233. |
| [8] | ZHU Z B, WEI Y, SHI M. Recent developments of cyclopropene chemistry[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2011, 40(11): 5534-5563. |
| [9] | BIANCHINI J, RALAIAMANERIVO A, GAYDOU E M. Determination of cyclopropenoic and cyclopropanoic fatty acids in cottonseed and kapok seed oils by gas-liquid chromatography[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1981, 53(13): 2194-2201. |
| [10] | 贾怡文, 陈小威, 孙尚德, 等. 气相色谱技术测定棉籽及其饼(粕)中环丙烯脂肪酸含量[J]. 中国油脂, 2022, 47(8): 121-127. |
| JIA Y W, CHEN X W, SUN S D, et al. Determination of cyclopropene fatty acids in cottonseed and its cake (meal) by gas chromatography[J]. China Oils and Fats, 2022,47(8): 121-127.(in Chinese) | |
| [11] | OBERT J C, HUGHES D, SORENSON W R, et al. A quantitative method for the determination of cyclopropenoid fatty acids in cottonseed, cottonseed meal, and cottonseed oil (Gossypium hirsutum) by high-performance liquid chromatography[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2007, 55(6): 2062-2067. |
| [12] | 黄龙会,石幸玉,谢海洲,等.基于化学衍生化的质谱技术在脂质分析中的研究进展[J].分析测试学报,2025,44(1):73-81. |
| HUANG L H, SHI X Y, XIE H Z, et al. Research progress on mass spectrometry techniques based on chemical derivatization for lipid analysis[J] Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 2025,44(1): 73-81.(in Chinese) | |
| [13] | LIU M, WEI F, LV X, et al. Rapid determination of aflatoxin B1 in medicinal and edible food by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Food Chemistry, 2018, 242: 338-344. |
| [14] | XIANG L, ZHU L, HUANG Y, et al. Application of derivatization in fatty acids and fatty acyls detection: Mass spectrometry-based targeted lipidomics[J]. Small Methods, 2020, 4(8): 2000160. |
| [15] | MANTZOURANI C, KOKOTOU M G. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) derivatization-based methods for the determination of fatty acids in biological samples[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(17): 5717. |
| [16] | 刘天宇, 张成龙, 杨瑞琴, 等. 衍生化在脂肪酸质谱分析中的应用研究进展[J]. 理化检验-化学分册, 2025,61(3), 364-372. |
| LIU T Y, ZHANG C L, YANG R Q, et al. Research progress on application of derivatization in mass spectrometry analysis of fatty acid[J]. Physical and Chemical Testing-Chemical Volume, 2025,61(3): 364-372.(in Chinese) | |
| [17] | FENG X H, WANG J, TANG Z H, et al. A strategy for accurately and sensitively quantifying free and esterified fatty acids using liquid chromatography mass spectrometry[J]. Frontiers in Nutrition, 2022, 9: 977076. |
| [18] | 陈喆, 云永欢, 马飞, 等. 基于特征脂肪酸的食用油中棉籽油掺假鉴别技术[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2023, 14(9): 122-127. |
| CHEN Z, YUN Y H, MA F, et al. Adulteration detection of edible oil with cottonseed oil based on characteristic fatty acid[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality, 2023, 14 (9): 122-127.(in Chinese) | |
| [19] | MITCHELL B, ROZEMA B, VENNARD T, et al. Determination of nutritional and cyclopropenoid fatty acids in cottonseed by a single GC analysis[J]. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 2015, 92(7): 947-956. |
| [20] | CRISCUOLO A, ZELLER M, COOK K, et al. Rational selection of reverse phase columns for high throughput LC-MS lipidomics[J]. Chemistry and Physics of Lipids, 2019, 221: 120-127. |
| [21] | 曹正, 李水军, 沈敏, 等. 液相色谱串联质谱临床检测方法的开发与验证[J]. 检验医学, 2019, 34(3): 189-196. |
| CAO Z, LI S J, SHEN M, et al. Consensus of method development and validation of liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in clinical laboratories[J]. Laboratory Medicine, 2019, 34(3), 189-196.(in Chinese) | |
| [22] | YANG A, ZHANG C, ZHANG B, et al. Effects of dietary cottonseed oil and cottonseed meal supplementation on liver lipid content, fatty acid profile and hepatic function in laying hens[J]. Animals (Basel), 2021, 11(1): 78. |
| [1] | FAN Qiuli, GOU Zhongyong, WANG Yitong, CUI Yan, LUO Qili, YE Jinling, LIN Xiajing, WANG Yibing, JIANG Shouqun. Effects of Fermented Mixed Meal on Growth Performance,Plasma Biochemical Indices and Meat Quality of Medium-growing Yellow-feathered Chickens [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2025, 52(9): 4069-4081. |
| [2] | LIN Xiajing, GOU Zhongyong, WANG Yibing, FAN Qiuli, YE Jinling, ZHANG Sai, JIANG Shouqun, RUAN Dong. Effects of Substituting Soybean Meal with Fermented Cottonseed Meal Equivalently on Growth Performance,Meat Quality and Antioxidation Activity of Yellow-Feathered Broilers [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2024, 51(7): 2890-2898. |
| [3] | NIU Junli, WEI Lianqing, ZHANG Wenju, NIE Cunxi. Effects of Fermented Cottonseed Meal on Growth Performance,Apparent Digestibility, Carcass Traits,and Lipid-related Indices in Broilers [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2020, 47(8): 2385-2394. |
| [4] | LUO Yuanqin, LU Yan, NIU Junli, WEI Lianqing, HE Ganggang, ZHENG Xinxia, LU Qicheng, NIU Yujie, ZHANG Wenju. Effects of Cottonseed Peptide-rich Fermented Cottonseed Meal on Growth Performance and Immune Functions in AA Broilers [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2020, 47(5): 1395-1403. |
| [5] | LEI Chenghong, CHEN Kaiyun, XU Xinfeng, HUDUSI·Aierken, XU Jun, BAI Meihua, SHI Qian, XIAO Yuanyuan, WANG Keke. Establishment of QuantStudioTM 3D Digital PCR Method for Detection of Equine Herpesvirus Type 1 [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2020, 47(5): 1299-1306. |
| [6] | LUO Yuanqin, HU Qian, LU Yan, ZHANG Fanfan, MA Guijun, LIU Jiancheng, ZHANG Wenju. A Studies on Nutrient Composition of Cotton Meal Fermented by Bacillus subtilis-1, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Their Compound Bacteria [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2020, 47(2): 452-459. |
| [7] | WEI Lianqing, NIU Junli, ZHAO Guanzheng, YU Jingzai, ZHANG Wenzhe, CHENG Hong, ZHANG Wenju, NIE Cunxi. Effects of Different Levels of Fermented Cottonseed Meal on Growth Performance, Slaughter Performance and Serum Biochemical Indexes of Cobb Broilers [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2019, 46(7): 1953-1961. |
| [8] | PENG Chengcheng, WU Yixiao, LIU Xuping, TAN Wensong. Study on Methods for Purification of H9N2 Subtype Avian Influenza Virus and Quantification of Viral HA Protein [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2019, 46(7): 2069-2078. |
| [9] | LIU Jiancheng, WU Chuanchuan, MA Guijun, ZHUO Mei, ZHANG Wenju. Nutritional Values of Fermented Cottonseed Meal and Its Application in Animal Production [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2018, 45(5): 1258-1265. |
| [10] | ZHANG Xiao-yang, ZHANG Wen-ju, WANG Yong-qiang, LIU Jian-cheng, NIE Cun-xi, YANG Liang. Effects of Cottonseed Meal Fermented by Lactobacillus acidophilus on Immune Function and Oxidation Resistance of Yellow-feathered Broilers [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2017, 44(8): 2311-2318. |
| [11] | MA Xi-shan, TANG Zhong-lin, XIAO Chong, YANG Bo-chao, QIN Chuan. Expression Analysis of THBS3 Gene in Different Tissues and Skeletal Muscles at Different Periods from Landrace and Tongcheng Pigs [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2016, 43(4): 1032-1038. |
| [12] | CHEN Ao-dong,KONG Ping,ZHAO Wei-li,HE Jia-wen,LIU Chen-li,GAO Wei. Comparative Analysis of Rumen Degradation Kinetics of Soybean Meal and Cottonseed Meal in the Ruminant [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2014, 41(5): 108-112. |
| [13] | WEI Bing-dong, DANG Xiu-li, QIU Yu-lang, CHEN Qun, LI Lin, LIU Hai-yan. Effect of Lactic Acid Bacteria Solid-state Fermentation on Crude Protein,pH,Acidity and Antinutritional Factor Content of Soybean Meal,Cottonseed Meal and Rapeseed Meal [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2014, 41(11): 107-114. |
| [14] | YAN Li-dong, ZHANG Wen-ju, NIE Cun-xi, JIANG Li-xin, MA Gui-jun, SUN Xin-wen. Effect of Fermented Cottonseed Meal Included on the Index of Blood Biochemistry and Immune Performance in Yellow-feathered Broilers [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2012, 39(10): 95-100. |
| [15] | FENG Li;ZHANG Wen-ju;YU Lei;SHI Guo-qing;. Optimization of Microelement Additive Amount in Substrate for Biological Protein Feed from Cottonseed Meal during Solid State Fermentation [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2011, 38(4): 30-32. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||