
China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine ›› 2026, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 776-786.doi: 10.16431/j.cnki.1671-7236.2026.02.024
• Nutrition and Feed • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Fei( ), PANG Xiaotong, GAO Zhentiao, NIE Cunxi(
), PANG Xiaotong, GAO Zhentiao, NIE Cunxi( )
)
Received:2025-08-06
Online:2026-02-20
Published:2026-01-27
Contact:
NIE Cunxi
E-mail:zhangfei_2023@163.com;niecunxi@sina.com
CLC Number:
ZHANG Fei, PANG Xiaotong, GAO Zhentiao, NIE Cunxi. Effects of Different Plant Extracts on Immune Function in Immunosuppressed Mice[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2026, 53(2): 776-786.
Table 1
Effects of plant extracts on body weight in immunosuppressed mice"
| 项目 Items | 初始体重 IBW | 第28天体重 Day 28 weight | 终末体重 FBW |
|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 Control group | 24.48±0.95 | 41.17±1.93 | 43.50±1.62ab |
| 环磷酰胺组 Cyclophosphamide group | 24.67±1.79 | 41.85±2.40 | 39.13±2.54c |
| 甜叶菊提取物组 Stevia extract group | 24.00±1.02 | 43.47±2.59 | 42.25±2.02abc |
| 金银花提取物组 Honeysuckle flower extract group | 24.82±2.03 | 46.17±1.88 | 45.18±2.02a |
| 黄芪提取物组 Astragalus extract group | 23.63±1.88 | 43.22±2.22 | 42.47±2.39abc |
| 葡萄籽原花青素提取物组 Grape seed proanthocyanidins extract group | 24.52±1.49 | 41.38±2.23 | 40.60±2.38bc |
| 甘草提取物组 Licorice extract group | 24.55±1.47 | 40.62±3.87 | 39.90±3.56bc |
| 辣椒碱提取物组 Capsaicin extract group | 24.27±1.47 | 43.88±2.08 | 43.15±2.46abc |
| P值 P-value | 0.892 | 0.112 | <0.001 |
Table 2
Effects of plant extracts on organ coefficient in immunosuppressed mice"
| 项目 Items | 肝脏指数 Liver index | 脾脏指数 Spleen index |
|---|---|---|
| 对照组 Control group | 4.82±0.37 | 0.31±0.13 |
| 环磷酰胺组 Cyclophosphamide group | 4.84±0.35 | 0.19±0.06 |
| 甜叶菊提取物组 Stevia extract group | 5.03±0.21 | 0.16±0.03 |
| 金银花提取物组 Honeysuckle flower extract group | 4.80±0.31 | 0.18±0.03 |
| 黄芪提取物组 Astragalus extract group | 4.67±0.26 | 0.23±0.02 |
| 葡萄籽原花青素提取物组 Grape seed proanthocyanidins extract group | 4.88±0.31 | 0.25±0.06 |
| 甘草提取物组 Licorice extract group | 4.49±0.57 | 0.17±0.05 |
| 辣椒碱提取物组 Capsaicin extract group | 4.97±0.61 | 0.22±0.07 |
| P值 P-value | 0.972 | 0.185 |
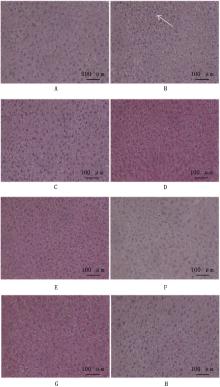
Fig.1
Effects of plant extracts on hepatic histomorphology in immunosuppressed mice (HE staining, 200×)①A, Control group; B, Cyclophosphamide group; C,Stevia extract group; D,Honeysuckle flower extract group; E,Astragalus extract group; F,Grape seed proanthocyanidins extract group; G,Licorice extract group; H,Capsaicin extract group. The same as below. ②White arrows indicate vacuolar enlargement in hepatocytes"

Table 3
Effects of plant extracts on serum immunoglobulin concentrations in immunosuppressed mice"
| 项目 Items | 免疫球蛋白A IgA | 免疫球蛋白G IgG | 免疫球蛋白M IgM |
|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 Control group | 61.40±6.51c | 694.38±59.13bc | 3.35±0.69 |
| 环磷酰胺组 Cyclophosphamide group | 58.51±6.13c | 610.63±48.93c | 2.83±0.60 |
| 甜叶菊提取物组 Stevia extract group | 60.41±7.61c | 631.88±55.38bc | 3.95±0.80 |
| 金银花提取物组 Honeysuckle flower extract group | 77.52±4.27b | 789.38±82.83bc | 4.05±0.79 |
| 黄芪提取物组 Astragalus extract group | 82.12±10.71ab | 816.88±90.31b | 4.14±0.99 |
| 葡萄籽原花青素提取物组 Grape seed proanthocyanidins extract group | 87.07±9.74ab | 779.38±88.98bc | 4.05±0.58 |
| 甘草提取物组 Licorice extract group | 89.05±6.00a | 746.88±91.07bc | 3.59±0.54 |
| 辣椒碱提取物组 Capsaicin extract group | 92.93±9.21a | 1 026.88±101.91a | 3.60±0.54 |
| P值 P-value | <0.001 | 0.001 | 0.185 |
Table 4
Effects of plant extracts on serum cytokine concentrations in immunosuppressed mice"
| 项目 Items | 肿瘤坏死因子α TNF-α | 白细胞介素6 IL-6 | 白细胞介素10 IL-10 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 Control group | 278.08±35.98cd | 101.25±29.21cd | 759.38±107.13b |
| 环磷酰胺组 Cyclophosphamide group | 240.38±68.77d | 93.75±17.42cd | 728.13±108.13b |
| 甜叶菊提取物组 Stevia extract group | 311.92±47.84cd | 134.31±8.48ab | 834.38±175.92b |
| 金银花提取物组 Honeysuckle flower extract group | 389.62±46.27bc | 148.47±28.10a | 1 094.38±183.31a |
| 黄芪提取物组 Astragalus extract group | 394.23±52.12bc | 99.31±10.08cd | 739.38±117.56b |
| 葡萄籽原花青素提取物组 Grape seed proanthocyanidins extract group | 541.92±78.57a | 82.08±16.62de | 771.88±114.70b |
| 甘草提取物组 Licorice extract group | 511.92±98.34ab | 70.97±14.25e | 795.63±143.99b |
| 辣椒碱提取物组 Capsaicin extract group | 453.46±48.24ab | 62.64±13.73e | 670.63±133.65b |
| P值 P-value | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.012 |
| [1] | JEFREMOW A, NEURATH M F. New agents for immunosuppression[J]. Best Practice & Research Clinical Gastroenterology, 2021, 54(55):101763. |
| [2] | 褚 席, 周宇飞, 刘爱玲, 等. 普洱茶多糖与儿茶素复合物对免疫抑制小鼠的保护作用[J]. 中国酿造, 2025, 44(6):171-177. |
| CHU X, ZHOU Y F, LIU A L, et al. Protective effect of Pu-erh tea polysaccharides and catechins compound on immunosuppressive mice[J]. China Brewing, 2025, 44(6):171-177. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | SUN N, YAN M, LIU X, et al. Polydatin alleviates cyclophosphamide-induced mouse immunosuppression by promoting splenic lymphocyte proliferation and thymic T cell development and differentiation[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2025, 26(6):2800. |
| [4] | FÁTIMA R, MACRCELA A N. Effects of plant extracts on human health[J]. Nutrients, 2025, 17(7):1229. |
| [5] | LI Z G, AN L J, ZHANG S J, et al. Structural elucidation and immunomodulatory evaluation of a polysaccharide from Stevia rebaudiana leaves[J]. Food Chemistry, 2021, 364:13031. |
| [6] | LEE H L, KIM J M, GO M J, et al. Protective effect of Lonicera japonica on PM2.5-induced pulmonary damage in BALB/c mice via the TGF-β and NF-κB pathway[J]. Antioxidants, 2023, 12(4): 968. |
| [7] | 王雪梅, 贾天玉, 管彬, 等. 黄芪多糖对免疫抑制模型小鼠Treg细胞及Th17细胞亚群的影响[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 2015, 27(1):153-157. |
| WANG X M, JIA T Y, GUAN B, et al. Effects of Astragalus polysaccharide on CD4+CD25+ Treg cells and Th17 cells in immunesuppressed mice[J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 2015, 27(1):153-157. (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | ZHOU K, YAN Z P, ZHOU K, et al. Effects of Huangqi Gancao decoction on intestinal immunity and microbiota in immunocompromised mice models[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2024, 15:1390170. |
| [9] | AN Q, GONG X X, LE L Q, et al. Prospects for Proanthocyanidins from grape seed: Extraction technologies and diverse bioactivity[J]. Food Reviews International, 2023, 39(1):349-368. |
| [10] | VIVEROS-PAREDES J M, PUEBLA-PÉREZ A M, GUTIÉRREZ-CORONADO O, et al. Capsaicin attenuates immunosuppression induced by chronic stress in BALB/c mice[J]. International Immunopharmacology, 2021, 93:107341. |
| [11] | 杨华青, 赵 磊, 徐美利, 等. 两种甜叶菊废渣提取物对D-半乳糖致衰老小鼠的抗氧化作用[J]. 中国食品学报, 2020, 20(10):34-42. |
| YANG H Q, ZHAO L, XU M L, et al. Antioxidant effect of two kinds of Stevia residue extracts on D-galactose induced aging mice[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2020, 20(10):34-42. (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 王 伟, 林宇城, 王玉兰, 等. 金银花茯苓提取物对小鼠免疫功能的在体调控作用[J]. 沈阳药科大学学报, 2022, 39(1):52-59. |
| WANG W, LIN Y C, WANG Y L, et al. Immunomodulatory effect of compound extract of Lonicerae japonicae flos and poria on mice[J]. Journal of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, 2022, 39(1):52-59. (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | 陈 垚. 茯苓、枸杞、黄芪提取物和海参冻干粉配伍增强免疫力作用的实验研究[J]. 中医临床研究, 2021, 13(1):1-5. |
| CHEN Y. An experimental study on efficacy of Fuling extract, Gouqi extract, Huangqi extract and freeze-dried sea cucumber powder on the immunity-enhancing[J]. Clinical Journal of Chinese Medicine, 2021, 13(1):1-5.(in Chinese) | |
| [14] | 伍 行, 吴凯鹏, 邵斯琪, 等. 葡萄籽原花青素对小鼠镇咳、祛痰及免疫增强作用的影响[J]. 湘南学院学报(医学版), 2022, 24(4):11-16. |
| WU H, WU K P, SHAO S Q, et al. Effects of grape seed proanthocyanidins on cough suppression,expectorant and immune enhancement in mice[J]. Journal of Xiangnan University(Medical Sciences), 2022, 24(4):11-16. (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | 吴国泰, 任 远, 马 骏, 等. 甘草甲醇提取物FM100对小鼠溃疡性结肠炎的药效学研究[J]. 中医儿科杂志, 2007, 5:14-17. |
| WU G T, REN Y, MA J, et al. The pharmacodynamics study of methanol extract of Glycyrrhizae FM100 on ulcerative colitis[J]. Journal of Pediatrics of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2007, 5:14-17. (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 范三红, 王娇娇, 李佳妮, 等. 辣椒红色素和辣椒碱体内抗氧化活性及降血脂功能[J]. 食品科学, 2021, 42(5):201-207. |
| FAN S H, WANG J J, LI J N, et al. In vivo antioxidant activity and hypolipidemic effect of capsanthin and capsaicin[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(5):201-207. (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | 徐倩倩, 杨万群, 王玉波, 等. 熟地黄多糖对环磷酰胺诱导的免疫抑制小鼠的免疫调节作用研究[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2023, 50(2):693-703. |
| XU Q Q, YANG W Q, WANG Y B, et al. Study on immunomodulatory effect of prepared Radix rehmanniae polysaccharide on cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppression in mice[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2023, 50(2):693-703. (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | DU X R, YAN Y H, DAI Y F, et al. Yogurt alleviates cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppression in mice through D-lactate[J]. Nutrients, 2024, 16(9):1395. |
| [19] | 王 伟, 林宇城, 王玉兰, 等. 金银花提取物对小鼠免疫功能的影响[J]. 沈阳药科大学学报, 2022, 39(2):164-173. |
| WANG W, LIN Y C, WANG Y L, et al. Effect of honeysuckle extract on the immune function in mice[J]. Journal of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, 2022, 39(2):164-173. (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | TATYANA N T, PETER J M. The liver is a metabolic and immunologic organ: A reconsideration of metabolic decompensation due to infection in inborn errors of metabolism (IEM)[J]. Molecular Genetics and Metabolism, 2017, 121(4):283-288. |
| [21] | 张凤丽, 马乳平, 黄文琪, 等. 菌草灵芝醇提物对免疫损伤小鼠脾脏和肠道菌群的调节作用[J/OL]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 1-15[2025-12-10]. |
| ZHANG F L, MA R P, HUANG W Q, et al. Regulatory effect of alcoholic extracts of JUNCAO Ganoderma lucidum on spleen and intestinal flora of immunoinjured mice[J/OL]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2025, 1-15[2025-12-10]. (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 李 巍, 陈贵才, 胡伟莲, 等. 丹参多糖低分子量组分抗小鼠肝肾损伤及对其免疫保护作用机制的研究[J]. 中国预防, 2023, 45(6):635-642. |
| LI W, CHEN G C, HU W L, et al. Ameliorative effect and mechanism of low-molecular-weight polysaccharide from Salvia miltiorrhiza against liver and kidney damage and immunosuppression[J]. Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 2023, 45(6):635-642. (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | HUANG H, XIE Y F, LI X F, et al. Danggui Buxue decoction regulates the immune function and intestinal microbiota of cyclophosphamide induced immunosuppressed mice[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2024, 15:1420411. |
| [24] | 王 燕, 朱晓庆, 谷新利, 等. 硒化甘草多糖对免疫抑制小鼠免疫功能的影响[J]. 饲料研究, 2023, 46(13):65-69. |
| WANG Y, ZHU X Q, GU X L, et al. Effect of selenide Glycyrrhiza polysaccharide on immune function of immunosuppressed mice[J]. Feed Research, 2023, 46(13):65-69. (in Chinese) | |
| [25] | 崔 怡, 乔凤杰, 邱嘉昊, 等. 灵芝酸A对刀豆球蛋白A诱导的急性免疫性肝损伤小鼠模型的影响及其作用机制[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2024, 40(12):2415-2423. |
| CUI Y, QIAO F J, QIU J H, et al. Effect of ganoderic acid A on a mouse model of concanavalin A-induced acute immune liver injury and its mechanism[J]. Journal of Clinical Hepatology, 2024, 40(12):2415-2423. (in Chinese) | |
| [26] | 李小丽. 葡萄籽原花青素治疗大鼠溃疡性结肠炎的作用机理研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2009. |
| LI X L. Therapeutic effect and mechanism of proanthocyanidins from grape seeds in rats with TNBS-induced ulcerative colitis[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2009. (in Chinese) | |
| [27] | 李 瑾, 刘冲英, 张婷婷, 等. 微波合成金银花硒多糖工艺及免疫活性研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2022, 47(14):3773-3780. |
| LI J, LIU C Y, ZHANG T T, et al. Synthesis of seleno-polysaccharides from Lonicerae japonicae flos via microwave and its immunological activity[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2022, 47(14):3773-3780. (in Chinese) | |
| [28] | 查苏娜, 苏日娜, 齐和日玛, 等. 刺玫根多糖对环磷酰胺诱导的免疫抑制小鼠的免疫调节作用[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 2024, 36(2):196-205. |
| CHA S N, SU R N, QIHERIMA, et al. Immunomodulatory effect of polysaccharides from Rosa davurica roots on immunosuppressed mice induced by cyclophosphamide[J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 2024, 36(2):196-205. (in Chinese) | |
| [29] | LAURA E C B, MARCELO B S, JAYAUM S B. Role of cellular effectors in the induction and maintenance of IgA responses leading to protective immunity against enteric bacterial pathogens[J]. Frontiers in Immunology, 2024, 15:1446072. |
| [30] | LOPANDIĆ Z, PROTIĆROSIĆ I, TODOROVIĆ A, et al. IgM and IgG immunoreactivity of SARS-CoV-2 recombinant M protein[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22(9):4951. |
| [31] | WOJNICKI S J, MORRIS A, SMITH B N, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of whole yeast cells and capsicum in weanling pigs challenged with pathogenic Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Animal Science, 2019, 97(4):1784-1795. |
| [32] | MORAES D C A, NAGI J G, FRITZEN J, et al. Effect of capsaicin on the feed intake and immunoglobin concentration of sows, and performance of piglets[J]. Tropical Animal Health and Production, 2022, 54(4):241. |
| [33] | 武新月, 张 薇, 俞 萍, 等. 紫苏桑叶金银花固体饮料对小鼠的免疫调节及抗突变作用[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2025, 51(17): 128-134.. |
| WU X Y, ZHANG W, YU P, et al. Immunomodulatory and anti-mutational effects of perilla and mulberry leaf and honeysuckle solid beverage in mice[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2025, 51(17): 128-134.(in Chinese) | |
| [34] | 白学鹏, 孙 鹏, 沈春秀, 等. 枸杞多糖对免疫抑制小鼠血清中IL-6、IL-10和IL-12/IL23 p40分泌水平的影响[J]. 动物医学进展, 2019, 40(7):49-51. |
| BAI X P, SUN P, SHEN C X, et al. Effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides on seral IL-6, IL-10 and IL-12/IL-23 p40 levels in sera of immunosuppressive mice[J]. Progress in Veterinary Medicine, 2019, 40(7):49-51. (in Chinese) | |
| [35] | 欧阳平, 彭立胜, 杨 红, 等. 重组人IL-10抑制TNF-α和PDGF-BB所致大鼠血管平滑肌细胞增殖[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2002, 12:35-38. |
| OUYANG P, PENG L S, YANG H, et al. Recombinant human interleukin-10 inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by TNF-α and PDGF-BB in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Pathophysiology, 2002, 12:35-38. (in Chinese) | |
| [36] | ZEBEAMAN M, TADESSE M G, BACHHETI R K, et al. Plants and plant-derived molecules as natural immunomodulators[J]. BioMed Research International, 2023, 1: 7711297. |
| [37] | 王 莹. 基于肠道微环境探讨金银花与山银花多糖的免疫调节作用差异[D]. 北京: 北京中医药大学, 2020. |
| WANG Y. Divergence in immunomodulatory effects between Lonicera japonica and Lonicera hypoglauca polysaccharides: An exploration based on gut microenvironment[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, 2020. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | HE Hang, HUANG Yuzhi, XIANG Bangquan, HAO Yongfeng, LIU Xingyu, ZHANG Jie, PENG Jinjin. Effects of Yeast Peptide on Immunity Function, Digestive Performance and Intestinal Microorganisms of Sichuan White Geese [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2025, 52(8): 3661-3671. |
| [2] | WANG Xueyang, LIN Zhan, LI Jiachen, XI Peng, ZHANG Hewei. Progress on Relationship Between Plant Extracts and Horizontal Transfer of Antibiotic Resistance Genes Carried by Plasmids [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2025, 52(7): 3479-3488. |
| [3] | WANG Haotian, LI Junzhe, MEI Xiaoying, LI Longxian, LI Yingying, ZHANG Mingrui, WU Yi. Effects of Cuscuta chinensis and Arctium lappa Compound Plant Extracts on Urine Physicochemical,Serum Antioxidant and Immune Indexes in Adult Cats [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2025, 52(6): 2531-2539. |
| [4] | ZHANG Guanfeng, SONG Xianfan, YAN Zhaoming, YANG Xiaojin, ZHENG Mengli, LIU Yating, CHEN Qinghua. Effects of Dietary Superoxide Dismutase Supplementation on Growth Performance, Immune Performance,Antioxidant Capacity and Intestinal Function of Broilers [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2025, 52(5): 1987-1998. |
| [5] | CAI Yucheng, WU Guanyuan, YANG Haidong, FANG Yinuo, CHEN Zhisheng, ZHAN Xiaoshu. Mechanisms and Current Applications of Probiotics in Animal Health Management [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2025, 52(5): 2101-2114. |
| [6] | BAI Lixia, LI Yang, LI Jianyong. Study on the Mechanism of Caffeic Acid Enhancing Macrophage Immunosuppression [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2025, 52(4): 1844-1851. |
| [7] | FAN Qiuli, TAO Zhengguo, LI Hui, GOU Zhongyong, WANG Yibing, LIN Xiajing, YE Jinling, JIANG Shouqun. Effects of α-mangostin on Growth Performance,Immune Function, Antioxidant Capacity and Detoxification Function of Broilers [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2025, 52(3): 1123-1130. |
| [8] | LI Jing, DONG Ying. Effects of Bacillus subtilis on Growth Performance,Intestinal Morphology, Serum Biochemical and Immune Indexes in Nursery Pigs [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2025, 52(2): 678-685. |
| [9] | LIU Shixiong, LI Xiao, LI Xueqiang, XU Zixuan, LI Songjian, DU Rui, XUE Chen, LIU Dacheng. Effects of Compound Bacteria Culture on Growth Performance,Immune Function and Vaccine Antibody Titer of Mongolian-Han Crossbred Mutton Sheep [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2025, 52(2): 718-729. |
| [10] | WANG Yuanzhuo, LIU Tong, WANG Guizhen, HAN Kunliang, GUO Hua. Effects of Compound Chinese Herb Ultrafine Powder on Immune Function and Related Gene Expression of Xinyang Black-feathered Laying Hens [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2025, 52(12): 5661-5669. |
| [11] | LI Lingui, YANG Zhenxiang, QIN Rongyan, LIU Yanfeng, ZHAO Linbo, WANG Lele, WANG Yan, WANG Wenqi. Effects of Coated Guanidine Glycolic Acid on Production Performance,Serum Biochemical Indicators,Antioxidant Capacity and Immune Function of Grazing Pregnant Ewes [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2025, 52(12): 5704-5714. |
| [12] | LI Zhenming, MA Xianyong, RONG Ting, CUI Yiyan, SONG Min, LIU Zhichang, DENG Dun, TIAN Zhimei, YU Miao. Effects of Guanidinoacetic Acid on Growth Performance,Serum Biochemical Indices,Antioxidant Capacity and Immune Function of Finishing Pigs [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2024, 51(8): 3311-3319. |
| [13] | RAN Yang, QIU Jie, SHEN Xiaoyun. Response of Fattening Hu Sheep to Cecropin Antimicrobial Peptides [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2024, 51(8): 3385-3393. |
| [14] | ZHANG Yan, MA Sen, LI Shouren, HUANGFU Weikang, LA Shaokai, MA Jixiang, WANG Zhichang, SHI Yinghua. Effects of Alfalfa Saponin Extract on Immunity,Antioxidant Capacity and Rumen Microflora of Weaned Hu Sheep [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2024, 51(7): 2799-2809. |
| [15] | DING Hui, LIU Xin, WANG Ruiling, MAO Yongxia, WANG Jiandong, GUO Yansheng. Effect of Dietary Addition of Soy Isoflavones on Production and Reproductive Performance of Angus Beef Cattle [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2024, 51(7): 2871-2879. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||